Hemodynamic responses to 1 MAC desflurane inhalation during anesthesia induction with propofol bolus and remifentanil continuous infusion: a prospective randomized single-blind clinical investigation
- PMID: 36814199
- PMCID: PMC9945592
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02002-6
Hemodynamic responses to 1 MAC desflurane inhalation during anesthesia induction with propofol bolus and remifentanil continuous infusion: a prospective randomized single-blind clinical investigation
Abstract
Background: Desflurane is not recommended during anesthesia induction because of its sympathetic stimulation effect, particularly in patients with myocardial ischemic disease. To date, the hemodynamic response to 1 MAC desflurane inhalation in combination with remifentanil infusion during anesthesia induction has rarely been reported.
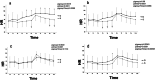
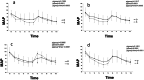
Methods: This investigation was designed to compare hemodynamic responses to 1 MAC desflurane (group D, n = 200) with sevoflurane (group S, n = 200) during anesthesia induction and endotracheal intubation in adult patients undergoing elective spine surgery. Subgroup analysis of the different age subgroups was also performed. With continuous infusion of remifentanil 0.1 μg/kg/min, anesthesia was induced with propofol bolus, and endotracheal intubation was performed after muscle relaxation. Heart rate (HR) and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) were measured every minute for 5 min after anesthesia induction (T1-5) and after endotracheal intubation (T6-10).
Results: HR was significantly higher in group D (n = 182) than in group S (n = 173) at T3-10 except at T6 (1 min after intubation) (all P < 0.05). In the age-based subgroup analyses, which subdivided the group D and S into four subgroups based on patient's age, the changes in HR from baseline values were significantly different between the coeval subgroups of patients in their 20-29 years and 30-39 years of age (all P < 0.05). MAP was reduced from baseline value, irrespective of group and age.
Conclusion: Inhalation of 1 MAC desflurane during anesthesia induction with propofol bolus and remifentanil continuous infusion and during endotracheal intubation was more likely to induce elevations in HR more likely than 1 MAC sevoflurane, especially in younger patients.
Trial registration: This study was registered in the Clinical Research Information Service (CRIS, http://cris.nih.go.kr ) of the Republic of Korea on Feb 12, 2016 (Registration No. KCT 0,001,813).
Keywords: Age; Desflurane; Hemodynamic response; Remifentanil; Sevoflurane.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

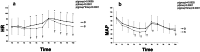
Similar articles
-
Remifentanil-propofol in vertebral disk operations: hemodynamics and recovery versus desflurane-n(2)o inhalation anesthesia.Adv Ther. 2007 May-Jun;24(3):622-31. doi: 10.1007/BF02848787. Adv Ther. 2007. PMID: 17660173 Clinical Trial.
-
Recovery of cognitive function after remifentanil-propofol anesthesia: a comparison with desflurane and sevoflurane anesthesia.Anesth Analg. 2000 Jan;90(1):168-74. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200001000-00035. Anesth Analg. 2000. PMID: 10624999 Clinical Trial.
-
Intraocular pressure more reduced during anesthesia with propofol than with sevoflurane: both combined with remifentanil.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002 Jul;46(6):703-6. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2002.460612.x. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002. PMID: 12059895 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of remimazolam on hemodynamic changes during cardiac ablation for atrial fibrillation under general anesthesia: a propensity-score-matched retrospective cohort study.Can J Anaesth. 2023 Sep;70(9):1495-1503. doi: 10.1007/s12630-023-02514-2. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Can J Anaesth. 2023. PMID: 37430181 Review. English.
-
Mechanistic consideration of the effect of perioperative volatile anesthetics on phagocytes.Clin Immunol. 2021 Jan;222:108635. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108635. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33217544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Desflurane attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating ITGB1/CD9 and reducing oxidative stress in tubular epithelial cells.Redox Biol. 2025 Mar;80:103490. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103490. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 39854938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiskopf RB, Moore MA, Eger EI, 2nd, et al. Rapid increase in desflurane concentration is associated with greater transient cardiovascular stimulation than with rapid increase in isoflurane concentration in humans. Anesthesiology. 1994;80(5):1035–1045. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199405000-00013. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

