Vitamin D status in healthy Italian school-age children: a single-center cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36814347
- PMCID: PMC9945672
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-023-01422-x
Vitamin D status in healthy Italian school-age children: a single-center cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D is involved in calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism, although its extra-skeletal actions are also well-known. Low serum 25(OH)D levels are common both in adults and children worldwide.
Methods: The purpose of this cross-sectional study was to determine the distribution of 25(OH)D levels in a cohort of healthy Italian school-age children, aged 5-10 years, in relationship to determinants of vitamin D deficiency such as season, BMI, gender, age and ethnicity.
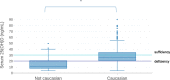
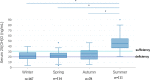
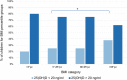
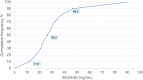
Results: The mean serum 25(OH) D level was 28.2 ng/mL; the prevalence of 25(OH)D sufficiency (> 30 ng/mL), insufficiency (20-30 ng/mL), deficiency (10-20 ng/mL) and severe deficiency (< 10 ng/mL) was 36%, 37%, 21% and 6% of the study-group population, respectively. The lower serum 25(OH)D values were observed during winter (21.6 ng/mL) and spring (22.9 ng/mL), as compared to summer (46.7 ng/mL) (p < 0.001). Higher BMI z-scores were associated with lower 25(OH)D level while no statistical difference was observed as related to gender and age groups.
Conclusions: Healthy Italian schoolchildren show low 25(OH)D levels, particularly during winter and spring time. Seasonality, ethnicity and overweight/obesity were confirmed to influence the vitamin D status, thus indicating the need for effective initiatives to support adequate vitamin D status in this population group.
Keywords: 25(OH) D; BMI; Deficiency; Prevalence; School-age children; Season; Vitamin D.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Saggese G, Vierucci F, Prodam F, Cardinale F, Cetin I, Chiappini E, et al. Vitamin D in pediatric age: consensus of the Italian Pediatric Society and the Italian Society of Preventive and Social Pediatrics, jointly with the Italian Federation of Pediatricians. Ital J Pediatr. 2018;44(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0488-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lionetti E, Galeazzi T, Dominijanni V, Acquaviva I, Naspi Catassi G, Iasevoli M, et al. Lower Level of Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Children at Diagnosis of Celiac Disease Compared with Healthy Subjects: A Case-Control Study. J Pediatr. 2021;228:132–137. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.08.089. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

