A chromosome-level genome assembly for Erianthus fulvus provides insights into its biofuel potential and facilitates breeding for improvement of sugarcane
- PMID: 36814384
- PMCID: PMC10363513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100562
A chromosome-level genome assembly for Erianthus fulvus provides insights into its biofuel potential and facilitates breeding for improvement of sugarcane
Abstract
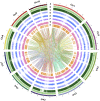
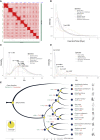
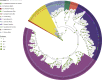
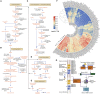
Erianthus produces substantial biomass, exhibits a good Brix value, and shows wide environmental adaptability, making it a potential biofuel plant. In contrast to closely related sorghum and sugarcane, Erianthus can grow in degraded soils, thus releasing pressure on agricultural lands used for biofuel production. However, the lack of genomic resources for Erianthus hinders its genetic improvement, thus limiting its potential for biofuel production. In the present study, we generated a chromosome-scale reference genome for Erianthus fulvus Nees. The genome size estimated by flow cytometry was 937 Mb, and the assembled genome size was 902 Mb, covering 96.26% of the estimated genome size. A total of 35 065 protein-coding genes were predicted, and 67.89% of the genome was found to be repetitive. A recent whole-genome duplication occurred approximately 74.10 million years ago in the E. fulvus genome. Phylogenetic analysis showed that E. fulvus is evolutionarily closer to S. spontaneum and diverged after S. bicolor. Three of the 10 chromosomes of E. fulvus formed through rearrangements of ancestral chromosomes. Phylogenetic reconstruction of the Saccharum complex revealed a polyphyletic origin of the complex and a sister relationship of E. fulvus with Saccharum sp., excluding S. arundinaceum. On the basis of the four amino acid residues that provide substrate specificity, the E. fulvus SWEET proteins were classified as mono- and disaccharide sugar transporters. Ortho-QTL genes identified for 10 biofuel-related traits may aid in the rapid screening of E. fulvus populations to enhance breeding programs for improved biofuel production. The results of this study provide valuable insights for breeding programs aimed at improving biofuel production in E. fulvus and enhancing sugarcane introgression programs.
Keywords: Erianthus fulvus; QTLs; SWEET family; biofuel; cold stress; reference genome.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of genome size and phylogenetic relationships of the Saccharum complex species.3 Biotech. 2022 Nov;12(11):327. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03338-5. Epub 2022 Oct 19. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 36276474 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of DREB1 transcription factors in Erianthus fulvus and the functional role of EfDREB1C in regulating cold tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis and sugarcane.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jun;317(Pt 1):144859. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.144859. Epub 2025 Jun 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40460955
-
EfGD: the Erianthus fulvus genome database.Database (Oxford). 2022 Aug 31;2022:baac076. doi: 10.1093/database/baac076. Database (Oxford). 2022. PMID: 36043401 Free PMC article.
-
Potential for Genetic Improvement of Sugarcane as a Source of Biomass for Biofuels.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 Nov 17;3:182. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00182. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26636072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Domestication to crop improvement: genetic resources for Sorghum and Saccharum (Andropogoneae).Ann Bot. 2007 Nov;100(5):975-89. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcm192. Epub 2007 Sep 1. Ann Bot. 2007. PMID: 17766842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Engineering for Enhancing Sugarcane Tolerance to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 24;13(13):1739. doi: 10.3390/plants13131739. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-quality haplotype-resolved chromosome assembly provides evolutionary insights and targeted steviol glycosides (SGs) biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Dec;22(12):3262-3277. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14446. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39283816 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease: Pathogenic Insights and Sustainable Management Approaches.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 7;14(4):508. doi: 10.3390/plants14040508. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Pattern of MYB Family Transcription Factors in Erianthus fulvus.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 25;14(12):2128. doi: 10.3390/genes14122128. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136950 Free PMC article.
-
The complete chloroplast genome of Saccharum fulvum (Poaceae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024 Mar 19;9(3):361-366. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2024.2327567. eCollection 2024. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024. PMID: 38516231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amalraj V., Balasundaram N.J. On the taxonomy of the members of ‘Saccharum Complex’. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2006;53:35–41.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

