Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after anlotinib treatment for small cell lung cancer: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 36814495
- PMCID: PMC9939648
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1126235
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after anlotinib treatment for small cell lung cancer: A case report and literature review
Abstract
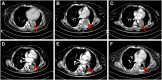
Anlotinib is an oral multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor as a third-line and subsequent treatment for patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) in China. The neurotoxicity is less reported. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is characterized by headaches, seizures, encephalopathy, and visual disturbances, as well as focal reversible vasogenic edema seen on neuroimages. Here, we presented a case of PRES in a small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patient associated with anlotinib. A 37-year-old female patient, who had a history of diabetes, with extensive-stage SCLC received anlotinib after third-line chemotherapy. Ten cycles of anlotinib later, the patient experienced visual disturbance and was diagnosed with PRES based on the typical demyelination of white matter obtained in the brain magnetic resonance. During anlotinib therapy, the patient did not develop anti-VEGF therapy-induced hypertension. Subsequently, the patient stopped anlotinib, but she did not recover from symptoms. We also summarized the characteristics of fifty-four cases of PRES caused by antiangiogenic drugs in the literature. Based on our experience and the literature review, the incidence of PRES induced by antiangiogenic drugs is low, and the symptom can resolve upon stopping the medications. However, some cases still have a poor prognosis and the underlying mechanism requires further investigation. In addition, early detection and treatment of PRES are essential for physicians.
Keywords: anlotinib; antiangiogenic therapy; case report; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; small cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Zou, Zhou, Lv, Liu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome associated with use of anlotinib to treat squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix: case report and literature review.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 15;14:1255785. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1255785. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38169843 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Associated With Anlotinib: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Neurol. 2021 May 6;12:546481. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.546481. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34025545 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) induced by pazopanib, a multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in a patient with soft-tissue sarcoma: case report and review of the literature.Invest New Drugs. 2018 Apr;36(2):346-349. doi: 10.1007/s10637-017-0521-5. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Invest New Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29067537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after lenvatinib treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 21;16:1487009. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1487009. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40191431 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with extensive cytotoxic edema after blood transfusion: a case report and literature review.BMC Neurol. 2018 Nov 12;18(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12883-018-1194-1. BMC Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30419835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zanubrutinib-induced aseptic meningitis: a case report and literature review.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1242491. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1242491. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37727390 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome associated with use of anlotinib to treat squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix: case report and literature review.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 15;14:1255785. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1255785. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38169843 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with Acalabrutinib, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor: a case report.Acta Neurol Belg. 2025 Apr;125(2):553-555. doi: 10.1007/s13760-024-02686-8. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Acta Neurol Belg. 2025. PMID: 39585523
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

