Trends in Rifampicin Resistance Among Children With Presumptive TB in the Pre-COVID and COVID-Era
- PMID: 36814532
- PMCID: PMC9939620
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X231156048
Trends in Rifampicin Resistance Among Children With Presumptive TB in the Pre-COVID and COVID-Era
Abstract
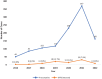
Publications on COVID-19's impact on the global tuberculosis burden are from adult cohorts, pediatric data are lacking for inform decision. We compared the TB trends in southern Nigerian children in the pre-COVID-19 and COVID-19 era. This was a retrospective, cross-sectional study of early morning sputum/gastric washing or stool samples from children with presumptive TB evaluated using GeneXpert in a tertiary hospital from January 2016 to May 2022. Of the 20 589 persons screened for presumed TB in the pre-COVID-19 and the COVID-19 era, only 1104 (88.7%) of 1245 children had complete data for analysis. In the COVID era, a significantly higher number of children were presumed to have TB 755 (68.4%), P < .001. The overall incidence of MTB detected by Xpert MTB/RIF during the study period was 6.4% (71/1104). The incidence of MTB in the pre-COVID-19 era was 24/349 (6.9%), which was slightly higher than the COVID-19 era (47/755; 6.2%), P > .05). The annual trends of MTB detected peaked in 2019 [18/115; 15.7%] in the pre-COVID-19 era, then plummeted to 12/228 (5.3%) in 2020 in the COVID-19 era, and reached its all-time low of 6/160 (3.8%) in the first half of 2022, (P < .001). The overall incidence of Rifampicin-resistant TB (RR-TB) was 2.8% among the MTB detected cases and all occurred in the COVID-19 era. This study found a significant decline in MTB diagnosis and in the emergence of RR-TB in the COVID-19 era. This necessitates re-prioritizing worldwide efforts to manage childhood tuberculosis, including increased testing, if the aim of eliminating tuberculosis by 2035 is to be met.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 era; children; pre-COVID-19; rifampicin resistance; tuberculosis.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2022. Accessed February 28, 2022. https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Torkington S. COVID-19: What you need to know about the coronavirus pandemic. World Economic Forum. 2022. Accessed June 15, 2022. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/06/covid-19-what-you-need-to-know-ab...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

