Variation of peripheral pulse transit time with internal vascular pressure changes induced by arm movement
- PMID: 36814792
- PMCID: PMC9939752
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1121902
Variation of peripheral pulse transit time with internal vascular pressure changes induced by arm movement
Abstract
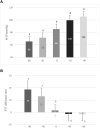
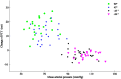
Pulse transit time (PTT) and blood pressure (BP) are widely used to quantify arterial characteristics. Arm position influences arterial BP and peripheral PTT. This study aims to quantify the relationship between PTT changes with internal vascular pressure variations induced by the arm moving. With left arm at horizontal position as reference and the right arm moving from 90 to 45, 0, -45, and -90° respectively, PTT difference was calculated by the difference of the pulse foot between right arm and left arm within the same heartbeat. The change in the BP was calculated from the gravitational effect with the measured arm length. Our results showed that the change in PTT with arm elevating is more obvious than that with arm lowering, indicating the different relationship between PTT changes due to the internal BP changes. This can help in understanding the inherent physiological/pathological mechanism of cardiovascular system.
Keywords: arm position; arterial blood pressure; arterial properties; hydrostatic principle; pulse transit time.
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Jiang, Wu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Atef M., Xiyan L., Wang G., Lian Y. (2016). “PTT based continuous-time non-invasive blood pressure system,” in IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (IEEE: ), 1–4. 10.1109/MWSCAS.2016.7870022 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

