Regulatory effects of IRF4 on immune cells in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 36814912
- PMCID: PMC9939821
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1086803
Regulatory effects of IRF4 on immune cells in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
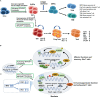
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is implicated in tumorigenesis, chemoresistance, immunotherapy failure and tumor recurrence. Multiple immunosuppressive cells and soluble secreted cytokines together drive and accelerate TME disorders, T cell immunodeficiency and tumor growth. Thus, it is essential to comprehensively understand the TME status, immune cells involved and key transcriptional factors, and extend this knowledge to therapies that target dysfunctional T cells in the TME. Interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) is a unique IRF family member that is not regulated by interferons, instead, is mainly induced upon T-cell receptor signaling, Toll-like receptors and tumor necrosis factor receptors. IRF4 is largely restricted to immune cells and plays critical roles in the differentiation and function of effector cells and immunosuppressive cells, particularly during clonal expansion and the effector function of T cells. However, in a specific biological context, it is also involved in the transcriptional process of T cell exhaustion with its binding partners. Given the multiple effects of IRF4 on immune cells, especially T cells, manipulating IRF4 may be an important therapeutic target for reversing T cell exhaustion and TME disorders, thus promoting anti-tumor immunity. This study reviews the regulatory effects of IRF4 on various immune cells in the TME, and reveals its potential mechanisms, providing a novel direction for clinical immune intervention.
Keywords: IRF4; T cell exhaustion; immunoregulation; immunosuppressive cells; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Lu, Liang, Li and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Essential role of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in immune cell development.Arch Pharm Res. 2016 Nov;39(11):1548-1555. doi: 10.1007/s12272-016-0854-1. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Arch Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27826752 Review.
-
An activating mutation of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in adult T-cell leukemia.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 4;293(18):6844-6858. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000164. Epub 2018 Mar 14. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29540473 Free PMC article.
-
IRF4 instructs effector Treg differentiation and immune suppression in human cancer.J Clin Invest. 2020 Jun 1;130(6):3137-3150. doi: 10.1172/JCI130426. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32125291 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of an IRF4 risk score to predict prognosis and response to immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Dec;113(Pt A):109411. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109411. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36461603
-
The diverse roles of IRF4 in late germinal center B-cell differentiation.Immunol Rev. 2012 May;247(1):73-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01113.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22500833 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data reveals a myeloid cell-related regulon predicting neoadjuvant immunotherapy response across cancers.J Transl Med. 2024 May 21;22(1):486. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05123-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38773508 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the genetic landscape of susceptibility to multiple primary cancers.HGG Adv. 2025 Apr 10;6(2):100413. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2025.100413. Epub 2025 Feb 4. HGG Adv. 2025. PMID: 39910817 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D3 reduces the expression of M1 and M2 macrophage markers in breast cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73152-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333342 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiome-derived bacterial lipids regulate gene expression of proinflammatory pathway inhibitors in systemic monocytes.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 26;15:1415565. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1415565. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38989285 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment of Burkitt lymphoma: different immune signatures with different clinical behavior.Blood Adv. 2024 Aug 27;8(16):4330-4343. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011506. Blood Adv. 2024. PMID: 38861355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carbó JM, León TE, Font-Díaz J, de la Rosa JV, Castrillo A, Picard FR, et al. . Pharmacologic activation of LXR alters the expression profile of tumor-associated macrophages and the abundance of regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res (2021) 81(4):968–85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3360 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

