FcγRI FG-loop functions as a pH sensitive switch for IgG binding and release
- PMID: 36814926
- PMCID: PMC9940316
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1100499
FcγRI FG-loop functions as a pH sensitive switch for IgG binding and release
Abstract
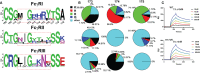
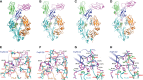
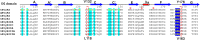
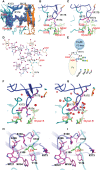
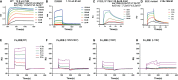
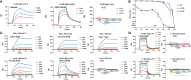
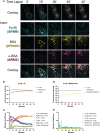
Understanding the molecular mechanism underlying the hierarchic binding between FcγRs and IgG antibodies is critical for therapeutic antibody engineering and FcγR functions. The recent determination of crystal structures of FcγRI-Fc complexes, however, resulted in two controversial mechanisms for the high affinity receptor binding to IgG. Here, we describe high resolution structures of a bovine FG-loop variant of FcγRI in complex with the Fc fragment of IgG1 crystallized in three different conditions at neutral pH, confirming the characteristic FG loop-Fc interaction is critical to the high affinity immunoglobulin binding. We showed that the FcγRI D2-domain FG-loop functioned as a pH-sensing switch for IgG binding. Further live cell imaging of FcγRI-mediated internalization of immune complexes showed a pH sensitive temporal-spatial antibody-antigen uptake and release. Taken together, we demonstrate that the structures of FcγRI-Fc crystallized at neutral and acidic pH, respectively, represent the high and low affinity binding states of the receptor for IgG uptake and release. These results support a role for FcγRI in antigen delivery, highlight the importance of Fc glycan in antibody binding to the high affinity receptor and provide new insights to future antibody engineering.
Keywords: Fc-glycan recognition; antibody recognition; human FcγRI; live cell tracking of FcγRI-antibody endocytosis; pH sensitive binding; receptor FG-loop.
Copyright © 2023 Lu, Spencer, Zou, Traver, Brzostowski and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure of FcγRI in complex with Fc reveals the importance of glycan recognition for high-affinity IgG binding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 20;112(3):833-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1418812112. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25561553 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of Fcγ receptor I and its implication in high affinity γ-immunoglobulin binding.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 25;286(47):40608-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.257550. Epub 2011 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21965667 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of the High Affinity IgG Receptor FcγRI Reduce Immune Complex Binding and Downstream Effector Functions.J Immunol. 2017 Oct 1;199(7):2432-2439. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601929. Epub 2017 Aug 16. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28814603
-
Structural mechanism of high affinity FcγRI recognition of immunoglobulin G.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):192-200. doi: 10.1111/imr.12346. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497521 Review.
-
The many faces of FcγRI: implications for therapeutic antibody function.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):160-74. doi: 10.1111/imr.12334. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497519 Review.
Cited by
-
Broadening anticancer spectrum by preprocessing and treatment of T- lymphocytes expressed FcγRI and monoclonal antibodies for refractory cancers.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 17;15:1400177. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1400177. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38953027 Free PMC article.
-
Guselkumab binding to CD64+ IL-23-producing myeloid cells enhances potency for neutralizing IL-23 signaling.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 12;16:1532852. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1532852. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40145093 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

