COVID-19 induced birth sex ratio changes in England and Wales
- PMID: 36814957
- PMCID: PMC9940645
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14618
COVID-19 induced birth sex ratio changes in England and Wales
Abstract
Background: The sex ratio at birth (male live births divided by total live births) may be a sentinel health indicator. Stressful events reduce this ratio 3-5 months later by increasing male fetal loss. This ratio can also change 9 months after major population events that are linked to an increase or decrease in the frequency of sexual intercourse at the population level, with the ratio either rising or falling respectively after the event. We postulated that the COVID-19 pandemic may have affected the ratio in England and Wales.
Methods: Publicly available, monthly live birth data for England and Wales was obtained from the Office for National Statistics up to December 2020. Using time series analysis, the sex ratio at birth for 2020 (global COVID-19 onset) was predicted using data from 2012-2019. Observed and predicted values were compared.
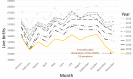
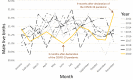
Results: From 2012-2020 there were 3,133,915 male and 2,974,115 female live births (ratio 0.5131). Three months after COVID-19 was declared pandemic (March 2020), there was a significant fall in the sex ratio at birth to 0.5100 in June 2020 which was below the 95% prediction interval of 0.5102-0.5179. Nine months after the pandemic declaration, (December 2020), there was a significant rise to 0.5171 (95% prediction interval 0.5085-0.5162). However, December 2020 had the lowest number of live births of any month from 2012-2020.
Conclusions: Given that June 2020 falls within the crucial window when population stressors are known to affect the sex ratio at birth, these findings imply that the start of the COVID-19 pandemic caused population stress with notable effects on those who were already pregnant by causing a disproportionate loss of male fetuses. The finding of a higher sex ratio at birth in December 2020, i.e., 9 months after COVID-19 was declared a pandemic, could have resulted from the lockdown restrictions that initially spurred more sexual activity in a subset of the population in March 2020.
Keywords: COVID-19; England; Lockdown; Population stressor; Sex ratio at birth; Sexual intercourse; Wales.
©2023 Masukume et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests. Witness Mapanga is employed by Wits Health Consortium (PTY) Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex Ratio at Birth in Northern Ireland During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison With Published Data From the Republic of Ireland, England and Wales.Am J Hum Biol. 2025 Jul;37(7):e70099. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.70099. Am J Hum Biol. 2025. PMID: 40579861 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 onset reduced the sex ratio at birth in South Africa.PeerJ. 2022 Aug 29;10:e13985. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13985. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36061753 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Sex Ratio at Birth in Ireland.Am J Hum Biol. 2024 Nov;36(11):e24159. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.24159. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Am J Hum Biol. 2024. PMID: 39324558
-
An estimation of intrapartum-related perinatal mortality rates for booked home births in England and Wales between 1994 and 2003.BJOG. 2008 Apr;115(5):554-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01669.x. BJOG. 2008. PMID: 18333936 Review.
-
The impact of catastrophic events on the sex ratio at birth: A systematic review.Am J Hum Biol. 2024 Apr;36(4):e24003. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.24003. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Am J Hum Biol. 2024. PMID: 37916952
Cited by
-
Sex Ratio at Birth after Concurrent Events of Earthquakes and the COVID-19 Pandemic in Croatia.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Apr 29;21(5):572. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21050572. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38791787 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing sex ratio at birth in Krosno, Poland.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):98. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50555-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38167565 Free PMC article.
-
Sex ratio at birth across 100 years in Sweden and risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality - a national register study.Eur J Epidemiol. 2024 Sep;39(9):967-976. doi: 10.1007/s10654-024-01137-1. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Eur J Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 39004637 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Ratio at Birth in Northern Ireland During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison With Published Data From the Republic of Ireland, England and Wales.Am J Hum Biol. 2025 Jul;37(7):e70099. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.70099. Am J Hum Biol. 2025. PMID: 40579861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bentall RP, Lloyd A, Bennett K, McKay R, Mason L, Murphy J, McBride O, Hartman TK, Gibson-Miller J, Levita L, Martinez AP, Stocks TVA, Butter S, Vallières F, Hyland P, Karatzias T, Shevlin M. Pandemic buying: testing a psychological model of over-purchasing and panic buying using data from the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. PLOS ONE. 2021;16:e0246339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246339. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical