Proximal Tibiofibular Joint Reconstruction With a Semitendinosus Allograft for Chronic Instability
- PMID: 36814978
- PMCID: PMC9939421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2022.08.052
Proximal Tibiofibular Joint Reconstruction With a Semitendinosus Allograft for Chronic Instability
Abstract
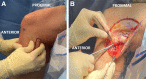
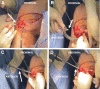
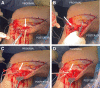
Whereas acute proximal tibiofibular joint (PTFJ) dislocation may require urgent reduction, chronic or recurrent instability may initially be approached with conservative treatment. Indications for PTFJ reconstruction include persistent lateral knee pain and/or tibiofibular instability for which conservative treatment has failed. Owing to the low incidence of diagnosed isolated PTFJ instability, there is still no consensus regarding the optimal surgical treatment, with an array of options having been previously described. We describe the treatment of isolated PTFJ instability using an anatomic reconstruction with semitendinosus allograft for chronic instability.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Anavian J., Marchetti D.C., Moatshe G., et al. The forgotten joint: Quantifying the anatomy of the proximal tibiofibular joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26:1096–1103. - PubMed
-
- See A., Bear R.R., Owens B.D. Anatomic mapping for surgical reconstruction of the proximal tibiofibular ligaments. Orthopedics. 2013;36:e58–e63. - PubMed
-
- Ogden J.A. Subluxation and dislocation of the proximal tibiofibular joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56:145–154. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

