[Bacterial resistance, a current crisis]
- PMID: 36815211
- PMCID: PMC10541255
[Bacterial resistance, a current crisis]
Abstract
Bacterial resistance is a constant battle representing a Public Health trouble. So much, that the World Health Organization considerate Public Health as a priority in health, due to the impact that generates as much as in health (giving that recent projections indicate that by 2050 it'll be produced more deaths because of this than the ones occasioned because of cancer) as its economic impact (which, according to a recent study in the United Kingdom, it'll cost the world's economy an estimated of 100 trillion dollars). The quick appearance of multidrug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria is a world nature phenomenon, questioning the antibiotics efficiency. Implement protocols and recommendations is essential, just as essential and necessary as give awareness to health personnel, taking as base the knowledge of resistance generation and its impact through the years, empowered by the actual pandemic of COVID 19.
La resistencia bacteriana es una constante batalla que representa un problema de Salud Pública. Tan es así que la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) la considera de sus prioridades en salud, debido al impacto que genera tanto en la salud (dado que proyecciones recientes indican que para 2050 se producirán más muertes por esta causa que las ocasionadas actualmente por el cáncer), como a su impacto económico (que, de acuerdo a un estudio reciente en el Reino Unido, costará a la economía mundial un estimado de 100 billones de dólares anualmente). La veloz aparición de bacterias multirresistentes y panresistentes es un fenómeno de índole mundial, cuestionando la eficacia antibiótica. Implementar protocolos y recomendaciones es vital, de igual forma que es necesario conciencias al personal sanitario, tomando como base el conocimiento de generación de resistencia y su impacto a través de los años, potenciado por la actual pandemia de la COVID-19.
Keywords: Anti-bacterial agents; COVID-19; Drug resistance; Drug resistance bacterial; Multidrug resistance; Spain.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


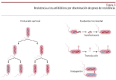
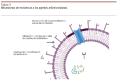
Similar articles
-
[Antimicrobial resistance: it is a global crisis, "a slow tsunami"].Ig Sanita Pubbl. 2019 Nov-Dec;75(6):429-450. Ig Sanita Pubbl. 2019. PMID: 32242168 Italian.
-
Part I Antimicrobial resistance: Bacterial pathogens of dermatologic significance and implications of rising resistance.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022 Jun;86(6):1189-1204. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.066. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35122894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A parallel and silent emerging pandemic: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) amid COVID-19 pandemic.J Infect Public Health. 2023 Apr;16(4):611-617. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2023.02.021. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Infect Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36857834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extremely and pandrug-resistant bacteria extra-deaths: myth or reality?Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Sep;37(9):1687-1697. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3300-0. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29956024 Review.
-
Late-onset neonatal infections and bacterial multidrug resistance.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2023 May 29;41:e2022068. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/2023/41/2022068. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37255111 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Melittin as Triple-Action Agent: Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities.Molecules. 2024 Jan 23;29(3):558. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030558. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338303 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfoglycodendron Antivirals with Scalable Architectures and Activities.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Sep 23;64(18):7141-7151. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00541. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 39230262
-
Epidemiological characteristics of antimicrobial use in Primary Care in Spain: a nationwide study.Rev Esp Quimioter. 2025 Mar 3;38(2):115-125. doi: 10.37201/req/120.2024. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2025. PMID: 39927581 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated Bacterial Identification with MALDI-TOF MS Leads to Fewer Diagnostic Tests and Cost Savings.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Dec 2;13(12):1163. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13121163. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766553 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfoglycodendron Antivirals with Scalable Architectures and Activities.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 18:2024.08.01.606251. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.01.606251. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Sep 23;64(18):7141-7151. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00541. PMID: 39131386 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abushaheen MA, Muzaheed M, Fatani AJ, Alosaimi M, Mansy W, George M et al. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Disease-a-Month. 2020 Jun 1;66(6). - PubMed
- Abushaheen MA, Muzaheed M, Fatani AJ, Alosaimi M, Mansy W, George M. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Disease-a-Month. 2020 Jun 01;66(6) - PubMed
-
- Al-Tawfiq JA, Momattin H, Al-Ali AY, Eljaaly K, Tirupathi R, Haradwala MB et al. Antibiotics in the pipeline: a literature review (2017-2020). Vol. 50, Infection. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH; 2022. p. 553-564. - PMC - PubMed
- Al-Tawfiq JA, Momattin H, Al-Ali AY, Eljaaly K, Tirupathi R, Haradwala MB. Antibiotics in the pipeline: a literature review (2017-2020) Infection. 2022;(50):553–564. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sengupta S, Chattopadhyay MK, Grossart HP. The multifaceted roles of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Front Microbiol. 2013;4(MAR):1-13. - PMC - PubMed
- Sengupta S, Chattopadhyay MK, Grossart HP. The multifaceted roles of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Front Microbiol. 2013;(4(MAR)):1–13. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vanegas-Múnera JM, Jiménez-Quiceno JN. Resistencia antimicrobiana en el siglo XXI: ¿hacia una era postantibiótica? Rev Fac Nac Salud Pública. Vol 38. No 1. 2020;1-6.
- Vanegas-Múnera JM, Jiménez-Quiceno JN. Resistencia antimicrobiana en el siglo XXI: ¿hacia una era postantibiótica? Rev Fac Nac Salud Pública. 2020;38(1):1–6.

