Impact of high-risk disease on the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma: a meta-analysis of 723 patients
- PMID: 36815380
- PMCID: PMC10542827
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2022.282510
Impact of high-risk disease on the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma: a meta-analysis of 723 patients
Figures
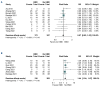

Comment in
-
CAR T-cell treatment of high-risk multiple myeloma: will there be a cure?Haematologica. 2023 Oct 1;108(10):2568-2569. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.282896. Haematologica. 2023. PMID: 36891744 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gagelmann N, Riecken K, Wolschke C, et al. . Development of CAR-T cell therapies for multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2020;34(9):2317-2332. - PubMed
-
- Munshi NC, Anderson LD, Shah N, et al. . Idecabtagene vicleucel in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):705-716. - PubMed
-
- Berdeja JG, Madduri D, Usmani SZ, et al. . Ciltacabtagene autoleucel, a B-cell maturation antigen-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CARTITUDE-1): a phase 1b/2 open-label study. Lancet. 2021;398(10297):314-324. - PubMed
-
- Gagelmann N, Ayuk F, Atanackovic D, Kröger N. B cell maturation antigen-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: a meta-analysis. Eur J Haematol. 2020;104(4):318-327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

