The role of Rapsyn in neuromuscular junction and congenital myasthenic syndrome
- PMID: 36815443
- PMCID: PMC10494853
- DOI: 10.17305/bb.2022.8641
The role of Rapsyn in neuromuscular junction and congenital myasthenic syndrome
Abstract
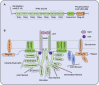
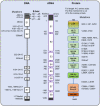
Rapsyn, an intracellular scaffolding protein associated with the postsynaptic membranes in the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), is critical for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor clustering and maintenance. Therefore, Rapsyn is essential to the NMJ formation and maintenance, and Rapsyn mutant is one of the reasons causing the pathogenies of congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS). In addition, there is little research on Rapsyn in the central nervous system (CNS). In this review, the role of Rapsyn in the NMJ formation and the mutation of Rapsyn leading to CMS will be reviewed separately and sequentially. Finally, the potential function of Rapsyn is prospected.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Musil L.S, Carr C, Cohen JB, Merlie JB. Acetylcholine receptor-associated 43K protein contains covalently bound myristate. J Cell Biol. 1988;107(3):1113–21. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.107.3.1113. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nghiem H.-O, Bettendorff L, Changeux J-P. Specific phosphorylation of Torpedo 43K rapsyn by endogenous kinase(s) with thiamine triphosphate as the phosphate donor. FASEB J. 2000;14(3):543–54. https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.14.3.543. - PubMed
-
- Gautam M, Mudd J, Copel NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Merlie JP. Characterization and mapping of the Rapsn gene encoding the 43-kDa acetylcholine receptor-associated protein. Genomics. 1994;24(2):366–9. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1994.1629. - PubMed
-
- Bukel A, Beeson D, James M, Vincent A. Cloning of cDNA encoding human rapsyn and mapping of the RAPSN gene locus to chromosome 11p11.2-p11.1. Genomics. 1996;35(3):613–6. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1996.0409. - PubMed
-
- Colledge M, Froehner SC. To muster a cluster: anchoring neurotransmitter receptors at synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95(7):3341–3. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.7.3341. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

