The Role of 18F-FDOPA PET/CT in Recurrent Medullary Thyroid Cancer Patients with Elevated Serum Calcitonin Levels
- PMID: 36815513
- PMCID: PMC9950688
- DOI: 10.4274/mirt.galenos.2022.81904
The Role of 18F-FDOPA PET/CT in Recurrent Medullary Thyroid Cancer Patients with Elevated Serum Calcitonin Levels
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the diagnostic performance of 18F-dihydroxyphenylalanine (FDOPA) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in the detection of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) recurrence in patients with elevated calcitonin levels.
Methods: The patients who had undergone 18F-FDOPA PET/CT imaging for elevated calcitonin levels after primary surgery of MTC were included in the study. addition, if available 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT and Gallium-68 (68Ga)- DOTATATE PET/CT images of the patients were evaluated retrospectively. The sensitivity and diagnostic performance of 18F-DOPA PET/CT were investigated.
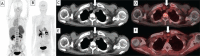
Results: A total of 14 patients (9 F and 5 M; median age: 45) were included in the analysis. Three patients had MEN IIA syndrome and 1 patient had MEN IIB syndrome, 10 patients had a diagnosis of sporadic MTC. Median calcitonin levels of the patients were calculated as 757.5 (min-max: 28.5-7911) pg/mL. Nine patients and 5 patients had undergone ultrasound and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (ceCT) of the neck, respectively, before 18F-FDOPA PET/CT imaging. 18F-FDOPA PET/CT revealed pathological uptake in the thyroid bed, lymph nodes, and distant organs in three, five and two patients, respectively. Median maximum standardized uptake value for the recurrent or metastatic lesions were calculated as 6.4 (min-max: 1.9-18.4). The sensitivity of 18F-FDOPA PET/CT in the detection of recurrent disease was calculated as 64%. Eight patients had 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT and 7 of them had 18F-FDG PET/CT within 3 months period before 18F-FDOPA PET/CT. 18F-FDOPA PET/CT revealed recurrent disease in 4 of 5 and 2 of the 5 patients who had negative 18F-FDG PET/CT and negative 68Ga- DOTATATE PET/CT, respectively.
Conclusion: 18F-FDOPA PET/CT can detect recurrence in about two- thirds of patients with elevated calcitonin levels after primary surgery for MTC. Due to variable differentiation degree, different receptor status, and clinical behavior of MTC, all three radiopharmaceuticals can be beneficial and are complementary to each other in patient management.
Amaç: Serum kalsitonin yüksekliği bulunan medüller tiroid kanseri (MTK) tanılı hastalarda rekürrensin saptanmasında 18F-dihidroksifenilalanin (FDOPA) pozitron emisyon tomografisi/bilgisayarlı tomografinin (PET/BT) performansının değerlendirilmesidir.
Yöntem: Primer MTK cerrahisi sonrasında yüksek kalsitonin düzeyi olan ve 18F-FDOPA PET/BT uygulanmış olan hastalar çalışmaya dahil edildi. Ek olarak, eğer varsa 18F-florodeoksiglukoz (FDG) PET/BT ve Galyum-68 (68Ga)-DOTATATE PET/BT bulguları da retrospektif olarak değerlendirildi.18F-FDOPA PET/BT’nin duyarlılığı ve tanısal performansı araştırıldı.
Bulgular: Toplam 14 hasta (9 K, 5 E, medyan yaş: 45) analize dahil edildi. Üç hastada MEN IIA, 1 hastada MEN IB sendromu, 10 hastada sporadik MTK mevcuttu. Hastaların medyan kalsitonin seviyeleri 757,5 (min-maks: 28.5-7911) pg/mL bulundu. 18F-FDOPA PET/BT görüntülemesinden önce 9 hastaya boyun ultrasonu, 5 hastaya kontrastlı boyun BT uygulanmıştı. 18F-FDOPA PET/BT’de 3 hastada tiroid yatağında nüks, 5 hastada lenf nodu metastazı ve 2 hastada uzak metastaz saptandı. Rekürren veya metastatik lezyonlarda medyan maksimum standartlaştırılmış alım değeri: 6,4 (min-maks: 1,9-18,4) olarak hesaplandı. Rekürren hastalığın saptanmasında 18F-FDOPA PET/BT’nin duyarlılığı %64 bulundu. 18F-FDOPA PET/BT’den önceki 3 ay içerisinde 8 hastanın 68Ga-DOTATATE, 7 hastanın 18F-FDG PET/BT görüntülemeleri mevcuttu. 18F-FDOPA PET/BT, negatif 18F-FDG PET/BT’si olan 5 hastanın 4’ünde ve negatif 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/BT’si olan 5 hastanın 2’sinde rekürren hastalığı gösterdi.
Sonuç: 18F-FDOPA PET/BT, MTK için primer cerrahi sonrası yüksek kalsitonin düzeyi bulunan hastaların yaklaşık 2/3’ünde rekürrens saptayabilir. Tiroid medüller karsinomunun değişken diferansiyasyon derecesi, farklı reseptör durumu ve klinik davranışına bağlı olarak, her üç radyofarmasötik de hasta yönetiminde faydalı olabilir ve birbirine tamamlayıcıdır.
Keywords: Medullary thyroid cancer; PET/CT; 18F-FDOPA; calcitonin.
©Copyright 2023 by Turkish Society of Nuclear Medicine Molecular Imaging and Radionuclide Therapy published by Galenos Yayınevi.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Pitt SC, Moley JF. Medullary, anaplastic, and metastatic cancers of the thyroid. Semin Oncol. 2010;37:567–579. - PubMed
-
- Machens A, Dralle H. Surgical treatment of medullary thyroid cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2015;204:187–205. - PubMed
-
- Pacini F, Castagna MG, Brilli L, Pentheroudakis G; ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Thyroid cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(Suppl 7):vii110–vii119. - PubMed
-
- Kloos RT, Eng C, Evans DB, Francis GL, Gagel RF, Gharib H, Moley JF, Pacini F, Ringel MD, Schlumberger M, Wells SA Jr; American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force. Medullary thyroid cancer: management guidelines of the American Thyroid Association. Thyroid. 2009;19:565–612. Erratum in: Thyroid 2009;19:1295. - PubMed
-
- Ong SC, Schöder H, Patel SG, Tabangay-Lim IM, Doddamane I, Gönen M, Shaha AR, Tuttle RM, Shah JP, Larson SM. Diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG PET in restaging patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma and elevated calcitonin levels. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:501–507. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
