Population Pharmacokinetics of Ganciclovir in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Patients
- PMID: 36815858
- PMCID: PMC10019199
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01550-22
Population Pharmacokinetics of Ganciclovir in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Patients
Abstract
Treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHCT) patients with ganciclovir is complicated by toxicity and resistance. This study aimed to develop an intravenous ganciclovir population pharmacokinetic model for post-alloHCT patients and to determine dosing regimens likely to achieve suggested therapeutic exposure targets. We performed a prospective observational single-center pharmacokinetic study in adult alloHCT patients requiring treatment with intravenous ganciclovir for CMV viremia or disease. Samples were analyzed using a validated ultraperformance liquid chromatography method. Population pharmacokinetic analysis and Monte Carlo simulations (n = 1000) were performed using Pmetrics for R. Twenty patients aged 18 to 69 years were included in the study. A 2-compartment model with linear elimination from the central compartment and between occasion variability best described the data. Incorporating creatinine clearance (CLCR) estimated by the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation and presence of continuous renal replacement therapy as covariates for ganciclovir clearance improved the model. Compared to current dosing recommendations, simulations demonstrated loading doses were required to achieve a target AUC24 of 80 to 120 mg.h/L on day 1 of induction therapy. Increased individualization of post-loading induction and maintenance doses based on CLCR is required to achieve the suggested exposures for efficacy (AUC24 >80/>40 mg.h/L for induction/maintenance) while remaining below the exposure thresholds for toxicity (AUC24 <120/<60 mg.h/L for induction/maintenance). Intravenous ganciclovir dosing in alloHCT patients can be guided by CLCR estimated by CKD-EPI. Incorporation of loading doses into induction dosing regimens should be considered for timely achievement of currently suggested exposures.
Keywords: allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation; cytomegalovirus; ganciclovir; pharmacokinetics; valganciclovir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


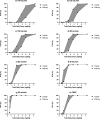
References
-
- Green ML, Leisenring W, Xie H, Mast TC, Cui Y, Sandmaier BM, Sorror ML, Goyal S, Özkök S, Yi J, Sahoo F, Kimball LE, Jerome KR, Marks MA, Boeckh M. 2016. Cytomegalovirus viral load and mortality after haemopoietic stem cell transplantation in the era of pre-emptive therapy: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Haematol 3:e119–e127. 10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00289-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hakki M, Aitken SL, Danziger-Isakov L, Michaels MG, Carpenter PA, Chemaly RF, Papanicolaou GA, Boeckh M, Marty FM. 2021. American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy Series: #3—prevention of cytomegalovirus infection and disease after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther 27:707–719. 10.1016/j.jtct.2021.05.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

