Changes in training activity post COVID-19 infection in recreational runners and cyclists
- PMID: 36815935
- PMCID: PMC9924504
- DOI: 10.17159/2078-516X/2022/v34i1a13758
Changes in training activity post COVID-19 infection in recreational runners and cyclists
Abstract
Background: Anecdotal evidence suggests that athletes struggle to return to exercise post COVID-19 infection. However, studies evaluating the effect of COVID-19 on athletes' exercise activity are limited.
Objectives: The objectives of this study were: (i) to describe the perceptions of recreational runners and cyclists recovering from COVID-19 on their training activity and general well-being, (ii) to compare device-measured training data in runners and cyclists pre- and post COVID-19, with non-infected controls that had a training interruption.
Methods: Participants who were recruited via social media completed an online questionnaire (n=61), including demographic, health and COVID-19 descriptive data. In a sub-sample, device-measured training data (heart rate, time, distance and speed, n=27) were obtained from GPS devices for four weeks before infection and on resumption of training. Similar data were collected for the control group (n=9) whose training had been interrupted but by factors excluding COVID-19.
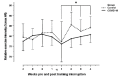
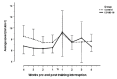
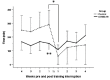
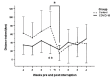
Results: Most participants experienced a mild to moderate illness (91%) that was associated with a training interruption time of two-four weeks. Decreases in heart rate, relative exercise intensity, speed, time and distance were observed during the first week of returning to training for both groups, followed by an increase from Week two onwards.
Discussion: Results failed to support a 'COVID-19 effect' on exercise activity as reductions in training variables occurred in both the COVID-19 and control groups. A possible explanation for the reductions observed is a deliberate gradual return to training by athletes post-COVID-19.
Conclusion: More research is needed using device-measured training data prior to and post COVID-19 infection to better understand the impact of the SARS-CoV-2 virus on the exercise activity of athletes.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; physical activity; relative exercise intensity; training activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest and source of funding: The authors declare no conflict of interest. This work is based on the research supported wholly by the National Research Foundation of South Africa (NRF) (MND200804549962).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protracted exercise tolerance post-coronavirus disease 2019 in endurance athletes: A survey.S Afr J Physiother. 2024 Aug 14;80(1):2063. doi: 10.4102/sajp.v80i1.2063. eCollection 2024. S Afr J Physiother. 2024. PMID: 39229293 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on training and technology use among Chilean amateur athletes.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Mar 11;6:1302023. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1302023. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 38529409 Free PMC article.
-
Training During the COVID-19 Lockdown: Knowledge, Beliefs, and Practices of 12,526 Athletes from 142 Countries and Six Continents.Sports Med. 2022 Apr;52(4):933-948. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01573-z. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34687439 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Changes and Recovery in Physical Function and Fitness After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus Infection: Implications for COVID-19 Rehabilitation.Phys Ther. 2020 Sep 28;100(10):1717-1729. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzaa129. Phys Ther. 2020. PMID: 32737507 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and Causes of Detraining in Athletes Due to COVID-19: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 28;19(9):5400. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095400. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protracted exercise tolerance post-coronavirus disease 2019 in endurance athletes: A survey.S Afr J Physiother. 2024 Aug 14;80(1):2063. doi: 10.4102/sajp.v80i1.2063. eCollection 2024. S Afr J Physiother. 2024. PMID: 39229293 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Impact of COVID-19 on Amateur Runners' Performance: An Analysis through Monitoring Devices.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;24(8):2635. doi: 10.3390/s24082635. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38676252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. World Health Organisation Coronavirus (COVID-19) Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2021. [(accessed 7 April 2021)]. https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus-covid-19 .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
