Identification of the core genes in Randall's plaque of kidney stone and immune infiltration with WGCNA network
- PMID: 36816033
- PMCID: PMC9931196
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1048919
Identification of the core genes in Randall's plaque of kidney stone and immune infiltration with WGCNA network
Abstract
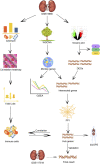
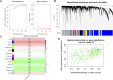
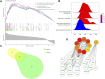
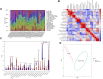
Background: Randall's plaque is regarded as the precursor lesion of lithiasis. However, traditional bioinformatic analysis is limited and ignores the relationship with immune response. To investigate the underlying calculi formation mechanism, we introduced innovative algorithms to expand our understanding of kidney stone disease. Methods: We downloaded the GSE73680 series matrix from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) related to CaOx formation and excluded one patient, GSE116860. In the RStudio (R version 4.1.1) platform, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified with the limma package for GO/KEGG/GSEA analysis in the clusterProfiler package. Furthermore, high-correlated gene co-expression modules were confirmed by the WGCNA package to establish a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. Finally, the CaOx samples were processed by the CIBERSORT algorithm to anchor the key immune cells group and verified in the validation series matrix GSE117518. Results: The study identified 840 upregulated and 1065 downregulated genes. The GO/KEGG results revealed fiber-related or adhesion-related terms and several pathways in addition to various diseases identified from the DO analysis. Moreover, WGCNA selected highly correlated modules to construct a PPI network. Finally, 16 types of immune cells are thought to participate in urolithiasis pathology and are related to hub genes in the PPI network that are proven significant in the validation series matrix GSE117518. Conclusion: Randall's plaque may relate to genes DCN, LUM, and P4HA2 and M2 macrophages and resting mast immune cells. These findings could serve as potential biomarkers and provide new research directions.
Keywords: CIBERSORT; Randall’s plaque; WGCNA (weighted gene co-expression network analyses); immune infiltration; kidney stone; renal calculi.
Copyright © 2023 Yu, Li, Jin, Su and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of the pivotal role of SPP1 in kidney stone disease based on multiple bioinformatics analysis.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Jan 11;15(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01157-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35016690 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of molecular mechanisms underlying kidney stones: gene expression profiles and potential diagnostic markers.Front Genet. 2024 Nov 13;15:1440774. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1440774. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39606015 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of uterine leiomyosarcoma-associated hub genes and immune cell infiltration pattern using weighted co-expression network analysis and CIBERSORT algorithm.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Jul 28;19(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02333-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34321013 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Randall plaques on kidney stone formation.Transl Androl Urol. 2014 Sep;3(3):251-4. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2014.07.03. Transl Androl Urol. 2014. PMID: 26816774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Randall's plaque and calcium oxalate stone formation: role for immunity and inflammation.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Jun;17(6):417-433. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-00392-1. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33514941 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis and validation of TP73 as a biomarker for calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis using machine learning and in vivo and in vitro experiments.Urolithiasis. 2024 Nov 16;52(1):164. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01655-3. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 39549053
-
Inhibition of NLRP3 alleviates calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal fibrosis and crystal adhesion.Urolithiasis. 2025 Mar 4;53(1):44. doi: 10.1007/s00240-025-01716-1. Urolithiasis. 2025. PMID: 40035889
-
Hypergraph-based analysis of weighted gene co-expression hypernetwork.Front Genet. 2025 Apr 4;16:1560841. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1560841. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40255486 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics identifies key genes and potential therapeutic targets in the pathological mechanism of oxidative stress in Randall's plaque.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31364. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82849-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Water R., Noordermeer C., van der Kwast T. H., Nizze H., Boevé E. R., Kok D. J., et al. (1999). Calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis: Effect of renal crystal deposition on the cellular composition of the renal interstitium. Am. J. kidney Dis. official J. Natl. Kidney Found. 33 (4), 761–771. 10.1016/s0272-6386(99)70231-3 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

