Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Ephedra Alata plant extract and a study of their antifungal, antibacterial activity and photocatalytic performance under sunlight
- PMID: 36816263
- PMCID: PMC9929317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13484
Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Ephedra Alata plant extract and a study of their antifungal, antibacterial activity and photocatalytic performance under sunlight
Abstract
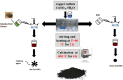
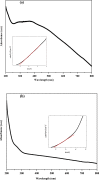
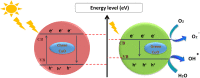
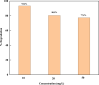
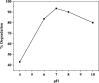
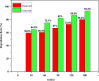
In the present work, copper oxide (CuO NPs) was synthesized by an eco-friendly, simple, low-cost, and economical synthesis method using Ephedra Alata aqueous plant extract as a reducing and capping agent. The biosynthesized CuO-NPs were compared with chemically obtained CuO-NPs to investigate the effect of the preparation method on the structural, optical, morphological, antibacterial, antifungal, and photocatalytic properties under solar irradiation. The CuO NPs were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-VIS spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) analysis, and field emission scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (FESEM-EDX). The photocatalytic activities of biosynthetic CuO-NPs and chemically prepared CuO-NPs were studied using methylene blue upon exposure to solar irradiation. The results showed that the biosynthesized CuO photocatalyst was more efficient than the chemically synthesized CuO-NPs for Methylene Blue (MB) degradation under solar irradiation, with MB degradation rates of 93.4% and 80.2%, respectively. In addition, antibacterial and antifungal activities were evaluated. The disk diffusion technique was used to test the biosynthesized CuO-NPs against gram-negative bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, as well as C. Albicans and S. cerevisiae. The biosynthesized CuO-NPs showed efficient antibacterial and antifungal activity. The obtained results revealed that the biosynthesized CuO-NPs can play a vital role in the destruction of pathogenic bacteria, the degradation of dyes, and the activity of antifungal agents in the bioremediation of industrial and domestic waste.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Antifungal activity; Biosynthesis; CuO-NPs; Ephedra Alata; Photocatalytic.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Abutilon indicum leaves extract and their evaluation of antibacterial, anticancer in human A549 lung and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.Food Chem Toxicol. 2022 Oct;168:113330. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113330. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35926645
-
An Eco-Friendly Synthesis Approach for Enhanced Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Properties of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Coelastrella terrestris Algal Extract.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 May 9;19:4137-4162. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S452889. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38756417 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of copper oxide and manganese oxide nanoparticles from watermelon seed shell extract for enhanced photocatalytic reduction of methylene blue.Int J Phytoremediation. 2023;25(6):789-798. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2022.2109588. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Int J Phytoremediation. 2023. PMID: 35976777
-
Green synthesis, characterization of silver nanoparticals for biomedical application and environmental remediation.J Microbiol Methods. 2022 Feb;193:106384. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106384. Epub 2021 Nov 23. J Microbiol Methods. 2022. PMID: 34826520 Review.
-
Plant extract-mediated green-synthesized CuO nanoparticles for environmental and microbial remediation: a review covering basic understandings to mechanistic study.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 Mar 19;7(9):2418-2445. doi: 10.1039/d5na00035a. eCollection 2025 Apr 29. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 40207087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Silver Nanoparticles Using Bioflocculant: A Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 May 15;11(5):492. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11050492. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Situ Synthesis of Cu2O Nanoparticles Using Eucalyptus globulus Extract to Remove a Dye via Advanced Oxidation.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jun 25;14(13):1087. doi: 10.3390/nano14131087. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998692 Free PMC article.
-
Galleria mellonella (Greater Wax Moth) as a Reliable Animal Model to Study the Efficacy of Nanomaterials in Fighting Pathogens.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jan 3;15(1):67. doi: 10.3390/nano15010067. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39791825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis of CuO nanoparticle using leaf extracts of Ocimum lamiifolium Hochst. ex Benth and Withana somnifera (L) Dunal for antibacterial activity.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 12;14(1):23870. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75296-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39396068 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its efficiency in degradation of rifampicin antibiotic.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 28;13(1):14030. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41119-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37640783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gusmão K.A.G., Gurgel L.V.A., Melo T.M.S., Gil L.F. Adsorption studies of methylene blue and gentian violet on sugarcane bagasse modified with EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD) in aqueous solutions: kinetic and equilibrium aspects. J. Environ. Manag. 2013;118:135–143. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.01.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khan I., Khan A.A., Khan I., Usman M., Sadiq M., Ali F., Saeed K. Investigation of the photocatalytic potential enhancement of silica monolith decorated tin oxide nanoparticles through experimental and theoretical studies. New J. Chem. 2020;44:13330–13343. doi: 10.1039/D0NJ00996B. - DOI
-
- Koffyberg F.P., Benko F.A. A photoelectrochemical determination of the position of the conduction and valence band edges of p‐type CuO. J. Appl. Phys. 1982;53:1173–1177. doi: 10.1063/1.330567. - DOI
-
- Weldegebrieal G.K. Photocatalytic and antibacterial activityof CuO nanoparticles biosynthesized using Verbascum thapsus leaves extract. Optik. 2020;204 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164230. - DOI
-
- B S B.M. Effect of precipitating agent NaOH on the preparation of copper oxide nanostructures for electrochemical applications. Наносистемы: Физика, Химия, Математика. 2016;7:482–487.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

