Chronic haloperidol administration downregulates select BDNF transcript and protein levels in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 36816400
- PMCID: PMC9932326
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1054506
Chronic haloperidol administration downregulates select BDNF transcript and protein levels in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkeys
Abstract
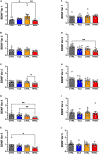
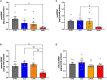
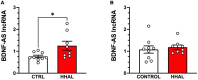
Post-mortem studies in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampal formation from schizophrenia patients have revealed significant disruptions in the expression molecules associated with cytoarchitecture, synaptic structure, function, and plasticity, known to be regulated in part by brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Interestingly, several studies using postmortem brain tissue from individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia have revealed a significant reduction in BDNF mRNA and protein levels in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), hippocampus and related areas; however, differentiating the effects of illness from antipsychotic history has remained difficult. We hypothesized that chronic antipsychotic treatment may contribute to the altered BDNF mRNA and protein expression observed in post-mortem brains of individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia. To address the influence of antipsychotic administration on BDNF expression in the primate brain, rhesus monkeys orally administered haloperidol, clozapine, or vehicle twice daily for 180 days. We found BDNF splice variants 4 and 5 in the DLPFC and variant 2 in the EC were significantly down-regulated following chronic administration of haloperidol. In addition, proBDNF and mature BDNF expression in the DLPFC, but not the EC, were significantly reduced. Based on the known regulation of BDNF expression by BDNF-AS, we assessed the expression of this lncRNA and found expression was significantly upregulated in the DLPFC, but not EC. The results of the present study provide evidence of haloperidol-induced regulation of BDNF mRNA and protein expression in the DLFPC and suggest an important role for BDNF-AS in this regulation. Given the role of BDNF in synaptic plasticity, neuronal survival and maintenance, aberrant expression induced by haloperidol likely has significant ramifications for neuronal populations and circuits in primate cortex.
Keywords: antipsychotic action; long non-coding RNA; messenger RNA (mRNA); neurotrophin (NT); non-human primate (macaque); protein; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2023 Hemby and McIntosh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AMPA receptor subunit and splice variant expression in the DLPFC of schizophrenic subjects and rhesus monkeys chronically administered antipsychotic drugs.Schizophr Res. 2007 Feb;90(1-3):28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.10.004. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Schizophr Res. 2007. PMID: 17141476 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF mRNA expression in rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex: effects of neonatal ventral hippocampal damage and antipsychotic drugs.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Jul;14(1):135-44. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2001.01633.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11488957
-
Region specific regulation of NR1 in rhesus monkeys following chronic antipsychotic drug administration.Biol Psychiatry. 2006 Sep 15;60(6):659-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.03.044. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Biol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16806093
-
Neurotrophic factors and CNS disorders: findings in rodent models of depression and schizophrenia.Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:151-65. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(03)46011-1. Prog Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14699963 Review.
-
Novel pharmacological approaches to the treatment of schizophrenia.Dan Med Bull. 2000 Jun;47(3):151-67. Dan Med Bull. 2000. PMID: 10913983 Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA-miRNA‒mRNA Network in Schizophrenia.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Aug 12;75(3):104. doi: 10.1007/s12031-025-02397-6. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40794250
-
Haloperidol, Olanzapine, and Risperidone Induce Morphological Changes in an In Vitro Model of Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 13;14(6):688. doi: 10.3390/biom14060688. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927091 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional evidence of reduced BDNF trophic capacity in the post-mortem human midbrain of schizophrenia cases with high inflammation.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 May 7;15(1):162. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03359-7. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40335479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold S, Hyman B, Van Hoesen G, Damasio A. Some cytoarchitectural abnormalities of the entorhinal cortex in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (1991) 48:625–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

