Anti-inflammatory or anti-SARS-CoV-2 ingredients in Huashi Baidu Decoction and their corresponding targets: Target screening and molecular docking study
- PMID: 36816510
- PMCID: PMC9928610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104663
Anti-inflammatory or anti-SARS-CoV-2 ingredients in Huashi Baidu Decoction and their corresponding targets: Target screening and molecular docking study
Abstract
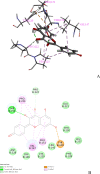
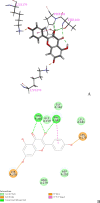
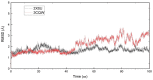
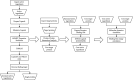
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a rapidly emerging infectious disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. Inflammatory factors may play essential roles in COVID-19 progression. Huashi Baidu Decoction (HSBD) is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula that can expel cold, dispel dampness, and reduce inflammation. HSBD has been widely used for the treatment of COVID-19. However, the active ingredients and potential targets for HSBD to exert anti-inflammatory or anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects remain unclear. In this paper, the active ingredients with anti-inflammatory or anti-viral effects in HSBD and their potential targets were screened using the Discovery Studio 2020 software. By overlapping the targets of HSBD and COVID-19, 8 common targets (FYN, SFTPD, P53, RBP4, IL1RN, TTR, SRPK1, and AKT1) were identified. We determined 2 key targets (P53 and AKT1) by network pharmacology. The main active ingredients in HSBD were evaluated using the key targets as receptor proteins for molecular docking. The results suggested that the best active ingredients Kaempferol2 and Kaempferol3 have the potential as supplements for the treatment of COVID-19.
Keywords: Active ingredient; Anti-SARS-CoV-2; Anti-inflammatory; COVID-19; Target; Traditional Chinese medicine formula.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computer-aided drug design combined network pharmacology to explore anti-SARS-CoV-2 or anti-inflammatory targets and mechanisms of Qingfei Paidu Decoction for COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 23;13:1015271. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1015271. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618410 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacological mechanism of Huashi Baidu Formula for the treatment of COVID-19 by combined network pharmacology and molecular docking.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Apr;10(4):3864-3895. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1759. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33691446
-
Analyzing the potential therapeutic mechanism of Huashi Baidu Decoction on severe COVID-19 through integrating network pharmacological methods.J Tradit Complement Med. 2021 Mar;11(2):180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Jan 18. J Tradit Complement Med. 2021. PMID: 33520684 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 and other viral infections: Efficacies and mechanisms.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Sep;225:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107843. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33811957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights for infection mechanism and potential targets of COVID-19: Three Chinese patent medicines and three Chinese medicine formulas as promising therapeutic approaches.Chin Herb Med. 2023 Apr;15(2):157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.06.014. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Chin Herb Med. 2023. PMID: 37220535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network pharmacology-based strategy to reveal the mechanism of pinocembrin against ovarian cancer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):3803-3815. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03492-y. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39361173
References
-
- Albarracin S.L., Stab B., Casas Z., Sutachan J.J., Samudio I., Gonzalez J., Gonzalo L., Capani F., Morales L., Barreto G.E. Effects of natural antioxidants in neurodegenerative disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 2012;15(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Banks W.A. From blood–brain barrier to blood–brain interface: new opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016;15(4):275–292. - PubMed
-
- Barabasi A.-L., Oltvai Z.N. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004;5(2):101–113. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
