The prognostic predictive value of systemic immune index and systemic inflammatory response index in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36816962
- PMCID: PMC9936064
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1006233
The prognostic predictive value of systemic immune index and systemic inflammatory response index in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To study the predictive value of systemic immune index (SII) and systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) in the prognosis of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
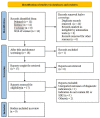
Methods: Two researchers independently searched PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and Web of Science databases (until March 18, 2022) for all studies on SII, SIRI, and prognosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Quality assessment of included studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). In addition, a bivariate mixed-effects model was used to explore predictive value.
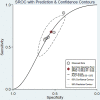
Results: A total of 9 studies that satisfied the requirements were included, involving, 3187 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The results of the meta-analysis showed that SII could be an independent predictor of OS (HR=1.78, 95%CI [1.44-2.20], Z=5.28, P<0.05), and SII could also be an independent predictor of PFS (HR=1.66, 95%CI [1.36-2.03], Z=4.94, P<0.05). In addition, SIRI could also serve as an independent predictor of OS (HR=2.88, 95%CI [1.97-4.19], Z=5.51, P<0.05). The ROC area was 0.63, the sensitivity was 0.68 (95%CI [0.55-0.78]), and the specificity was 0.55 (95%CI [0.47-0.62]), all of which indicated that SII had a certain predictive value for OS.
Conclusion: SII and SIRI can be used as independent predictors to predict the prognosis and survival status of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and have certain predictive accuracy. Therefore, SII and SIRI should be considered in studies that update survival risk assessment systems.
Systematic review registration: https://www.ytyhdyy.com/, identifier PROSPERO (CRD42022319678).
Keywords: meta-analysis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; prognosis; systemic immune index; systemic inflammatory response index.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Qin, Zhang, Xue and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, et al. The eighth edition ajcc cancer staging manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "Personalized" approach to cancer staging. CA: A Cancer J Clin (2017) 67(2):93–9. doi: 10.3322/caac.21388 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

