HIF‑1α inhibits ferroptosis and promotes malignant progression in non‑small cell lung cancer by activating the Hippo‑YAP signalling pathway
- PMID: 36817050
- PMCID: PMC9932041
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2023.13676
HIF‑1α inhibits ferroptosis and promotes malignant progression in non‑small cell lung cancer by activating the Hippo‑YAP signalling pathway
Abstract
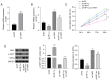
Ferroptosis and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) have critical roles in human tumors. The aim of the present study was to investigate the associations between ferroptosis, HIF-1α and cell growth in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. The lung cancer cell lines SW900 and A549 were evaluated using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) to detect the expression of HIF-1α. Cell Counting Kit-8, flow cytometry and Transwell migration assays were used to measure cell viability, apoptosis and invasion, respectively. The production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH) and ferrous ion (Fe2+) were determined using detection kits. The expression levels of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) and Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) were detected using RT-qPCR and western blotting. The results showed that the expression of HIF-1α was significantly upregulated in NSCLC cells compared with normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Small interfering RNA specific to HIF-1α (si-HIF-1α) significantly decreased the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells and increased their apoptosis. si-HIF-1α also increased the levels of ROS, MDA and Fe2+ but decreased GSH and GPX4 levels in A549 cells. Additionally, si-HIF-1α increased phosphorylated (p-)YAP1 levels, suppressed GPX4 and YAP1 expression, and attenuated the YAP1 overexpression-induced changes in YAP1, p-YAP1 and GPX4 levels and cell viability. The ferroptosis antagonist ferrostatin-1 partially attenuated the effects of si-HIF-1α on the NSCLC cells, while the ferroptosis agonist erastin further inhibited NSCLC growth by blocking HIF-1α expression. In conclusion, the silencing of HIF-1α induces ferroptosis by suppressing Hippo-YAP pathway activation in NSCLC cells. The present study provides novel insights into the malignant progression of NSCLC and suggests that HIF-1α is an effective target for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: Hippo-YAP pathway; ferroptosis; hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; non-small cell lung cancer; oxidative stress.
Copyright: © Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Fashoyin-Aje LA, Fernandes LL, Sridhara R, Keegan P, Pazdur R. Demographic composition of lung cancer trials: FDA analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36((15_suppl)):S9088. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.9088. - DOI
-
- Goodgame B, Viswanathan A, Zoole J, Gao F, Miller CR, Subramanian J, Meyers BF, Patterson AG, Govindan R. Risk of recurrence of resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer in elderly patients as compared with younger patients. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4:1370–1374. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181b6bc1b. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
