A Case of Hepatic Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 36817074
- PMCID: PMC9935885
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/2271690
A Case of Hepatic Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
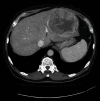
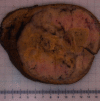
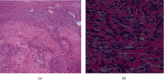
A 73-year-old man with a history of atrial myxoma and basal cell carcinoma presented with unexplained fever. Contrast-enhanced CT abdomen showed a large left hepatic lobe mass with early enhancement and delayed venous washout, concerning for hepatocellular carcinoma. Fine needle aspiration showed numerous spindle cells with malignant nuclear features, suggestive of malignant spindle cell neoplasm. The patient underwent left hepatectomy. The surgical specimen showed a well-circumscribe solid mass (14.6 × 13.0 × 10.0 cm) with necrosis. Histopathological examination revealed a proliferation of spindle tumor cells with characteristic staghorn-shaped blood vessels, frequent mitoses, and necrosis. The tumor cells showed strong and diffuse expression of CD34 and STAT6, confirming the diagnosis of malignant solitary fibrous tumor. Solitary fibrous tumor is a rare fibroblastic tumor characterized by a staghorn vasculature and NAB2-STAT6 gene rearrangement. Solitary fibrous tumor of the liver is a rare occurrence. Although most solitary fibrous tumors behave in a benign fashion, solitary fibrous tumors might act aggressively. This case is unique in that it demonstrates an excellent correlation between radiologic, macroscopic, and microscopic features which can contribute to the improvement of radiologic and pathologic diagnostic accuracy.
Copyright © 2023 Zhiyan Fu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Odze R. D., Cree I. A., Klimstra D. S., et al. WHO Classification of Tumours. Digestive System Tumours . Fifth. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer press; 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

