Brain grey and white matter structural associations with future suicidal ideation and behaviors in adolescent and young adult females with mood disorders
- PMID: 36817186
- PMCID: PMC9937714
- DOI: 10.1002/jcv2.12118
Brain grey and white matter structural associations with future suicidal ideation and behaviors in adolescent and young adult females with mood disorders
Abstract
Background: To reduce suicide in females with mood disorders, it is critical to understand brain substrates underlying their vulnerability to future suicidal ideation and behaviors (SIBs) in adolescence and young adulthood. In an international collaboration, grey and white matter structure was investigated in adolescent and young adult females with future suicidal behaviors (fSB) and ideation (fSI), and without SIBs (fnonSIB).
Methods: Structural (n = 91) and diffusion-weighted (n = 88) magnetic resonance imaging scans at baseline and SIB measures at follow-up on average two years later (standard deviation, SD = 1 year) were assessed in 92 females [age(SD) = 16.1(2.6) years] with bipolar disorder (BD, 28.3%) or major depressive disorder (MDD, 71.7%). One-way analyses of covariance comparing baseline regional grey matter cortical surface area, thickness, subcortical grey volumes, or white matter tensor-based fractional anisotropy across fSB (n = 40, 43.5%), fSI (n = 33, 35.9%) and fnonSIB (n = 19, 20.6%) groups were followed by pairwise comparisons in significant regions (p < 0.05).
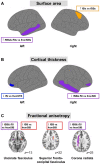
Results: Compared to fnonSIBs, fSIs and fSBs showed significant decreases in cortical thickness of right inferior frontal gyrus pars orbitalis and middle temporal gyrus, fSIs of left inferior frontal gyrus, pars orbitalis. FSIs and fSBs showed lower fractional anisotropy in left uncinate fasciculus and corona radiata, and fSBs in right uncinate and superior fronto-occipital fasciculi.
Conclusions: The study provides preliminary evidence of grey and white matter alterations in brain regions subserving emotional and behavioral regulation and perceptual processing in adolescent and young adult females with mood disorders with, versus without, future SIBs. Findings suggest potential targets to prevent SIBs in female adolescents and young adults.
Keywords: adolescence; gender; magnetic resonance imaging; mood disorder; suicidal behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Hilary P. Blumberg received an honorarium for a talk at Aetna. The remaining authors have declared that they have no competing or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Avants, B. B. , Tustison, N. , & Song, G. (2009). Advanced normalization tools (ANTS). Insight Journal, 2(365), 1–35.
-
- Behrens, T. E. J. , Woolrich, M. W. , Jenkinson, M. , Johansen‐Berg, H. , Nunes, R. G. , Clare, S. , Matthews, P. , Brady, J. , & Smith, S. (2003). Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion‐weighted MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 50(5), 1077–1088. 10.1002/mrm.10609 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benjamini, Y. , & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 57(1), 289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous