Water deprivation induces hypoactivity in rats independently of oxytocin receptor signaling at the central amygdala
- PMID: 36817576
- PMCID: PMC9928579
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1062211
Water deprivation induces hypoactivity in rats independently of oxytocin receptor signaling at the central amygdala
Abstract
Introduction: Vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OXT) are neuropeptides produced by magnocellular neurons (MCNs) of the hypothalamus and secreted through neurohypophysis to defend mammals against dehydration. It was recently demonstrated that MCNs also project to limbic structures, modulating several behavioral responses.
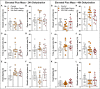
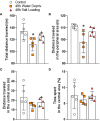
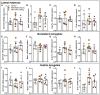
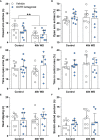
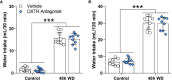
Methods and results: We found that 24 h of water deprivation (WD) or salt loading (SL) did not change exploration or anxiety-like behaviors in the elevated plus maze (EPM) test. However, rats deprived of water for 48 h showed reduced exploration of open field and the closed arms of EPM, indicating hypoactivity during night time. We evaluated mRNA expression of glutamate decarboxylase 1 (Gad1), vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (Slc17a6), AVP (Avpr1a) and OXT (Oxtr) receptors in the lateral habenula (LHb), basolateral (BLA) and central (CeA) amygdala after 48 h of WD or SL. WD, but not SL, increased Oxtr mRNA expression in the CeA. Bilateral pharmacological inhibition of OXTR function in the CeA with the OXTR antagonist L-371,257 was performed to evaluate its possible role in regulating the EPM exploration or water intake induced by WD. The blockade of OXTR in the CeA did not reverse the hypoactivity response in the EPM, nor did it change water intake induced in 48-h water-deprived rats.
Discussion: We found that WD modulates exploratory activity in rats, but this response is not mediated by oxytocin receptor signaling to the CeA, despite the upregulated Oxtr mRNA expression in that structure after WD for 48 h.
Keywords: central amygdala; dehydration; elevated plus maze test; exploratory behavior; oxytocin receptor.
Copyright © 2023 Felintro, Trujillo, dos-Santos, da Silva-Almeida, Reis, Rocha and Mecawi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hernandez VS, Hernandez OR, Perez de la Mora M, Gomora MJ, Fuxe K, Eiden LE, et al. . Hypothalamic vasopressinergic projections innervate central amygdala gabaergic neurons: Implications for anxiety and stress coping. Front Neural Circuits (2016) 10:92. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2016.00092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

