Magnetic marker localisation in breast cancer surgery
- PMID: 36817668
- PMCID: PMC9897082
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2020.93673
Magnetic marker localisation in breast cancer surgery
Abstract
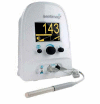
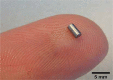
Since mammographic screening programmes were initiated, the spectrum of breast cancer has changed in terms of impalpable tumours, thus causing the development of new localisation methods, including magnetic markers. We offer herein an up-to-date review focused on two magnetic markers (Magseed, MaMaLoc) currently used in breast cancer surgery for the localisation of breast tumours or pathological axillary nodes. Magnetic marker localisation presents a safe and reliable method for breast tumour marking. Four currently available prospective studies demonstrate that the Magseed system has a negative margin rate and a successful localisation rate, both of which are comparable to standard marking systems used in breast cancer surgery. The main benefits of magnetic markers are that they require no radiation safety measures, and they offer the possibility of longer deployment times, thus simplifying surgery scheduling. The most important drawbacks are cost of the system, depth limitation and need for frequent probe recalibration.
Keywords: MaMaLoc; Magseed; breast cancer surgery; impalpable breast tumour; magnetic marker.
Copyright: © 2020 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

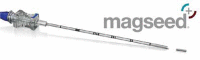

References
-
- Wyld L, Markopoulos C, Leidenius M, Senkus-Konefka E (eds.). Breast Cancer Management for Surgeons: A European Multidisciplinary Textbook. Springer International Publishing; 2018.
-
- Patel SN, Mango VL, Jadeja P, et al. . Reflector-guided breast tumor localization versus wire localization for lumpectomies: a comparison of surgical outcomes. Clin Imaging 2018; 47: 14-7. - PubMed
-
- Spalluto LB, DeBenedectis CM, Morrow MS, Lourenco AP. Advances in breast localization techniques: an opportunity to improve quality of care and patient satisfaction. Semin Roentgenol 2018; 53: 270-9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
