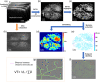
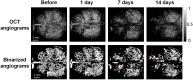
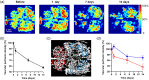
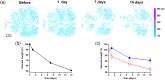
In vivo characterization of cerebrovascular impairment induced by amyloid β peptide overload in glymphatic clearance system using swept-source optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 36817752
- PMCID: PMC9933996
- DOI: 10.1117/1.NPh.10.1.015005
In vivo characterization of cerebrovascular impairment induced by amyloid β peptide overload in glymphatic clearance system using swept-source optical coherence tomography
Abstract
Significance: Antiamyloid ( ) immunotherapy is a promising therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease (AD) but generates large amounts of soluble peptides that could overwhelm the clearance pathway, leading to serious side effects. Direct implications of in glymphatic drainage transport for cerebral vasculature and tissue are not well known. Studies are needed to resolve this issue and pave the way to better monitoring abnormal vascular events that may occur in -modifying therapies for AD.
Aim: The objective is to characterize the modification of cerebral vasculature and tissue induced by soluble abundantly present in the glymphatic clearance system.
Approach: peptide was injected intracerebroventricularly and swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) was used to monitor the progression of changes in the brain microvascular network and tissue in vivo over 14 days. Parameters reflecting vascular morphology and structure as well as tissue status were quantified and compared before treatment.
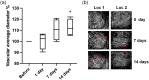
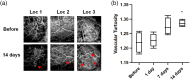
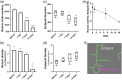
Results: Vascular perfusion density, vessel length, and branch density decreased sharply and persistently following peptide administration. In comparison, vascular average diameter and vascular tortuosity were moderately increased at the late stage of monitoring. Endpoint density gradually increased, and the global optical attenuation coefficient value decreased significantly over time.
Conclusions: burden in the glymphatic system directly contributes to cerebrovascular structural and morphological abnormalities and global brain tissue damage, suggesting severe deleterious properties of soluble cerebrospinal fluid- . We also show that OCT can be used as an effective tool to monitor cerebrovascular dynamics and tissue property changes in response to therapeutic treatments in drug discovery research.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid β; cerebrovasculature; glymphatic system; optical coherence tomography.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures