Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of end-stage renal disease: A nationwide, population-based study
- PMID: 36817794
- PMCID: PMC9932810
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1116489
Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of end-stage renal disease: A nationwide, population-based study
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the risk of incident chronic kidney disease among the patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the association of RA and the risk of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) has not been clearly elucidated. We aimed to investigate the association of RA and the risk of ESRD.
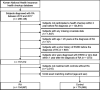
Materials and methods: A total of 929,982 subjects with (n = 154,997) or without (n = 774,985) RA from the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database in Koreas (corresponding to the period between 2009 and 2017) were retrospectively analyzed. RA was defined by the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM), codes plus any dispensing of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. The primary outcome was incident ESRD, identified by a combination of the ICD-10-CM codes and a special code assigned to patients receiving maintenance dialysis for ≥ 3 months or those with a transplant kidney.
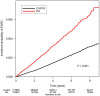
Results: Compared to the subjects without RA, the subjects with RA resulted in an increased incidence of ESRD (incidence rates of 0.374 versus 0.810 cases per 1,000 person-years). Accordingly, compared to the subjects without RA, the risk of ESRD was significantly increased among the subjects with RA (adjusted hazard ratio 2.095, 95% confidence interval 1.902-2.308). Subgroup analyses revealed that the risk of ESRD imposed by RA is relatively higher in relatively young and healthy individuals.
Conclusion: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) increase the risk of ESRD. As the risk of ESRD imposed by RA is relatively higher in relatively young and healthy individuals, kidney-protective treatment, such as biologic agents, should be preferentially considered among these patients with RA.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; end-stage renal disease; nation-wide population-based study; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2023 Suh, Jung, Oh, Yang, Choi, Kim, Bae, Ma, Han and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary: Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of end-stage renal disease: a nationwide, population-based study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 25;10:1194649. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1194649. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37305132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials