The Effect of Occupational Stress and Concerns about the COVID-19 Pandemic on Secondary Traumatic Stress Syndrome among Iranian Frontline Nurses: A Mediating Model
- PMID: 36817816
- PMCID: PMC9922346
- DOI: 10.18502/ijps.v17i4.10685
The Effect of Occupational Stress and Concerns about the COVID-19 Pandemic on Secondary Traumatic Stress Syndrome among Iranian Frontline Nurses: A Mediating Model
Abstract
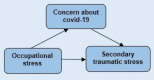
Objective: With the increasing effects of stress caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and occupational stress on the mental health of frontline nurses, it is imperative to further investigate how these stresses affect nurses' mental health and secondary traumatic stress syndrome. This research aimed to investigate the relationship of nurses' occupational stress and concerns about COVID-19 with secondary traumatic stress syndrome, and also to investigate the mediating effect that concerns about the COVID-19 pandemic have on the relationship between nurses' occupational stress and secondary traumatic stress syndrome. Method : A cross-sectional design was adopted. The population of the study was defined as all front-line nurses in Shiraz hospitals, from which 225 nurses of two corona care hospitals were selected using convenience sampling. The degree of secondary traumatic stress, concerns about the COVID-19, and nurses' occupational stress were assessed using Bride's Secondary Traumatic Stress Scale (STSS), an adopted version of Level of Concerns about the COVID-19 questionnaire, and the Nurses' Occupational Stressor Scale (NOSS) among Hospital-based Healthcare Workers. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to examine the relationships among variables. Results: Results showed that nurses' occupational stresses presented a direct effect on nurses' level of concern about the COVID-19 pandemic (β = 0.85, P < 0.001), and concern about the COVID-19 pandemic was directly related to front-line nurse's secondary traumatic stress syndrome (β = 0.83, P < 0.001). In addition, nurses' level of concern about the COVID-19 pandemic fully mediated the effects of nurses' occupational stresses on their secondary traumatic stress (β = 0.70, P < 0.001). This indirect effect has explained 68% of the variance in nurses' secondary traumatic stress. Conclusion: These results emphasized the indirect effect of nurses' occupational stresses on secondary traumatic stress syndrome via mediating the level of concern about COVID-19. Therefore, to reduce the secondary traumatic stress of nurses who have dealt directly with COVID-19 patients, it seems necessary to pay serious attention to the sources of their occupational stress, which probably existed even before this pandemic and increased their concerns in pandemic conditions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Nurses; Occupational Stress; Secondary Traumatic Stress.
Copyright © 2022 Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of perceived organizational support and ego-resilience on the relationship between occupational stressors and compassion fatigue in COVID-19 frontline nurses: a cross-sectional study in Sichuan, China.BMC Nurs. 2024 Nov 11;23(1):817. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02473-z. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39529080 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on front-line nurses' professional quality of life.Nurs Manag (Harrow). 2023 Jan 24. doi: 10.7748/nm.2023.e2074. Online ahead of print. Nurs Manag (Harrow). 2023. PMID: 36691712
-
The effect of stress levels of nurses on performance during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of motivation.J Res Nurs. 2022 Jun;27(4):330-340. doi: 10.1177/17449871211070982. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Res Nurs. 2022. PMID: 35837263 Free PMC article.
-
Nurses' Emotional Stress Levels When Caring for COVID-19 Patients in an Intensive Care Unit.Altern Ther Health Med. 2021 Sep;27(5):46-50. Altern Ther Health Med. 2021. PMID: 34144534 Review.
-
[Covid-19 and front-line nurses' mental health: a literature review].Prof Inferm. 2021 Jan-Mar;74(1):41-47. doi: 10.7429/pi.2021.741041. Prof Inferm. 2021. PMID: 34089640 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Exposure to secondary traumatic stress and its related factors among emergency nurses in Saudi Arabia: a mixed method study.BMC Nurs. 2024 May 18;23(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02018-4. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38762742 Free PMC article.
-
Sociodemographic Factors, Mental Health, and Emotional Eating Associated With Concern for COVID-19 Contagion in Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Prim Care Community Health. 2023 Jan-Dec;14:21501319231200400. doi: 10.1177/21501319231200400. J Prim Care Community Health. 2023. PMID: 37731344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO, 2020) Archived from the original on 31 January 2020. [Accessed 30 January 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-...
-
- Guterres, A. UN leads call to protect most vulnerable from mental health crisis during and after COVID-19. UN News. 2020. Available from: https://news.un.org/feed/view/en/story/2020/05/1063882.
-
- Bambi S, Iozzo P, Lucchini A. New Issues in Nursing Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Italy. Am J Crit Care. 2020;29(4):e92–e3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
