3D bio-printed living nerve-like fibers refine the ecological niche for long-distance spinal cord injury regeneration
- PMID: 36817821
- PMCID: PMC9931763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.01.023
3D bio-printed living nerve-like fibers refine the ecological niche for long-distance spinal cord injury regeneration
Abstract
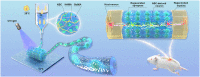
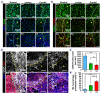
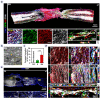
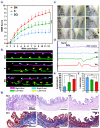
3D bioprinting holds great promise toward fabricating biomimetic living constructs in a bottom-up assembly manner. To date, various emergences of living constructs have been bioprinted for in vitro applications, while the conspicuous potential serving for in vivo implantable therapies in spinal cord injury (SCI) has been relatively overlooked. Herein, living nerve-like fibers are prepared via extrusion-based 3D bioprinting for SCI therapy. The living nerve-like fibers are comprised of neural stem cells (NSCs) embedded within a designed hydrogel that mimics the extracellular matrix (ECM), assembled into a highly spatial ordered architecture, similar to densely arranged bundles of the nerve fibers. The pro-neurogenesis ability of these living nerve-like fibers is tested in a 4 mm-long complete transected SCI rat model. Evidence shows that living nerve-like fibers refine the ecological niche of the defect site by immune modulation, angiogenesis, neurogenesis, neural relay formations, and neural circuit remodeling, leading to outstanding functional reconstruction, revealing an evolution process of this living construct after implantation. This effective strategy, based on biomimetic living constructs, opens a new perspective on SCI therapies.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; Hydrogels; Living constructs; Neural stem cells; Spinal cord injury.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

