Driving Hazard Perception Components: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36818054
- PMCID: PMC9923031
- DOI: 10.30476/BEAT.2023.95410.1356
Driving Hazard Perception Components: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the rate of driving hazard perception (HP), explicate the content of HP and determine its components.
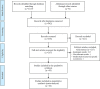
Methods: The present study is a systematic review and a meta-analysis which is carried out to gather data, to search Science Direct, PubMed, Scopus, PROQUEST, web of knowledge databases, Google scholar search engine and also to search manually from January 2000 to September 2021 with using related keywords. EndNote X20 software was used to manage and screening studies. Stata16 was used for meta-analysis. Thematic content analysis was used to analyze the findings. The entire review process was conducted by two authors, and disputes were referred to a third person.
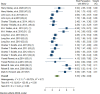
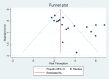
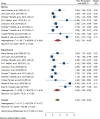
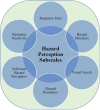
Results: Out of the 1167 founded articles, 50 were finally included in the study. According to 10 imported papers for meta-analysis includes 2770 sample size, general HP of drivers is estimated 3.33 [4.04-2.62 with CI 95, I2=89.72]. Also, HP for experienced and beginner drivers is estimated 3.26 [2.23-4.26 with CI 95, I2=89.47] and 3.42 [2.41-4.43 with CI 95, I2=89.68], respectively. Also, in the data meta-synthesis, 28 definitions of HP and 6 main components are identified to evaluate HP using thematic content analysis.
Conclusion: In this study, obtained results show that all people need constant and gradual training at all levels. A factor that can be effective to improve drivers' HP is to make drivers to take training courses and to pass standard tests at the time of obtaining driving license.
Keywords: Automobile drivers; Component.; Hazard; Perception; Traffic accident.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest the authors state they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Driving Hazard Perception Tests: A Systematic Review.Bull Emerg Trauma. 2023;11(2):51-68. doi: 10.30476/BEAT.2023.95777.1370. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2023. PMID: 37193008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research on drivers' hazard perception in plateau environment based on visual characteristics.Accid Anal Prev. 2022 Mar;166:106540. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2021.106540. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Accid Anal Prev. 2022. PMID: 34958979
-
Are interventions effective at improving driving in older drivers?: A systematic review.BMC Geriatr. 2020 Apr 3;20(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12877-020-01512-z. BMC Geriatr. 2020. PMID: 32245367 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of hazard perception characteristics based on driving behavior considering overt and covert hazard scenarios.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 1;17(4):e0266126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266126. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35363815 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
Cited by
-
Enhancing Driving Safety through User Experience Evaluation of the C-ITS Mobile Application: A Case Study of the DARS Traffic Plus App in a Driving Simulator Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 30;24(15):4948. doi: 10.3390/s24154948. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123994 Free PMC article.
-
Pilot Study on Gaze Characteristics of Older Drivers While Watching Driving Movies.Geriatrics (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;9(5):132. doi: 10.3390/geriatrics9050132. Geriatrics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451864 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hazards and sensation-seeking on intermediate swimming college students' hazard perceptions.Brain Behav. 2023 Dec;13(12):e3338. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3338. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 38031238 Free PMC article.
-
Driving Hazard Perception Tests: A Systematic Review.Bull Emerg Trauma. 2023;11(2):51-68. doi: 10.30476/BEAT.2023.95777.1370. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2023. PMID: 37193008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hutton A, Savage C, Ranse J, Finnell D, Kub J. The use of Haddon’s matrix to plan for injury and illness prevention at outdoor music festivals. Prehospital and disaster medicine. 2015;30(2):175–83. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman K, Jinadasa D, Maegga B, Guerrero A. Road traffic injury on rural roads in Tanzania: measuring the effectiveness of a road safety program. Traffic injury prevention. 2015;16(5):456–60. - PubMed
-
- Organization W H. European regional status report on road safety 2019. 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
