Socioeconomic status and problem behaviors in young Chinese children: A moderated mediation model of parenting styles and only children
- PMID: 36818114
- PMCID: PMC9936862
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1029408
Socioeconomic status and problem behaviors in young Chinese children: A moderated mediation model of parenting styles and only children
Abstract
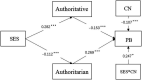
Introduction: This study tested a moderated mediation model of child number (CN) and parenting styles (PS) in the relationships between family socioeconomic status (SES) and young children's problem behaviors (PB).
Methods: A sample of 1,101 children (Mage = 4.90 years, SD = 1.07) and their parents participated in this study. Parents reported on PS, SES, and children's PB.
Results and discussion: The results show SES was positively related to authoritative parenting and negatively related to authoritarian parenting; problem behaviors were negatively related to authoritative parenting and positively related to authoritarian parenting; authoritative parenting and authoritarian parenting mediated the relationship between SES and PB; and singleton moderated the relationship between SES and PB. The combination of only children and low levels of SES could lead to high PB levels, while the combination of non-only children and high levels of SES could lead to high PB levels. At the same SES, only children had higher PB levels than non-only children.
Keywords: SES; child number; moderated mediation; parenting styles; problem behaviors; young children.
Copyright © 2023 Lin, Zhang, Liao and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Parenting style and Chinese preschool children's pre-academic skills: A moderated mediation model of approaches to learning and family socioeconomic status.Front Psychol. 2023 Feb 6;14:1089386. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1089386. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36814671 Free PMC article.
-
Family socioeconomic status and young children digital addiction: a moderated mediation model.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 27;15:1435575. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1435575. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39399265 Free PMC article.
-
Parenting styles, food-related parenting practices, and children's healthy eating: A mediation analysis to examine relationships between parenting and child diet.Appetite. 2018 Sep 1;128:205-213. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2018.06.021. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Appetite. 2018. PMID: 29920321 Free PMC article.
-
The integrative role of parenting styles and parental involvement in young children's science problem-solving skills.Front Psychol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1096846. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1096846. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37377695 Free PMC article.
-
Parenting styles and the dietary intake of pre-school children: a systematic review.Psychol Health. 2020 Nov;35(11):1326-1345. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2020.1743842. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Psychol Health. 2020. PMID: 32255381
Cited by
-
Raising Generation Z Children in China: Parenting Styles and Psychosocial Adjustment.Psychosoc Interv. 2025 May 9;34(2):103-115. doi: 10.5093/pi2025a9. eCollection 2025 May. Psychosoc Interv. 2025. PMID: 40385638 Free PMC article.
-
Parenting style and children emotion management skills among Chinese children aged 3-6: the chain mediation effect of self-control and peer interactions.Front Psychol. 2023 Sep 18;14:1231920. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1231920. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37790239 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of family socioeconomic status on college students' mental health literacy: the chain mediating effect of parenting styles and interpersonal relationships.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1477221. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1477221. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39539306 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Relationship Between Aggressive Behavior, Family Parenting Styles, and Self-Esteem Among Only-Child College Students in China: A Cross-Sectional Study.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2025 Feb 26;18:435-448. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S505802. eCollection 2025. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2025. PMID: 40026338 Free PMC article.
-
Intergenerational Parenting Styles and Children's Problem Behaviors: The Mediating Role of the Grandparent-Parent Relationship.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Jul 29;15(8):1029. doi: 10.3390/bs15081029. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alizadeh S., Talib M. B. A., Abdullah R., Mansor M. (2011). Relationship between parenting style and children’s behavior problems. Asian Soc. Sci. 7, 195–200. doi: 10.5539/ass.v7n12p195 - DOI
-
- Barber B. K., Olsen J. A. (1997). Socialization in context: connection, regulation, and autonomy in the family, school, and neighborhood, and with peers. J. Adolesc. Res. 12, 287–315. doi: 10.1177/0743554897122008 - DOI
-
- Baumrind D. (1966). Effects of authoritative parental control on child behavior. Child Dev. 37, 887–907. doi: 10.2307/1126611 - DOI
-
- Baumrind D. (1971). Current patterns of parental authority. Dev. Psychol. 4, 1–103. doi: 10.1037/h0030372 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

