Effect of exercise on renal function in diabetic nephropathy-a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36818178
- PMCID: PMC9906014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.11.002
Effect of exercise on renal function in diabetic nephropathy-a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Diabetic nephropathy causes cardiovascular complications among individuals with diabetes which results in decreased kidney function and overall physical decline. The objective of this systematic review was to determine effects of exercise on various renal function parameters amond individuals with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. It was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42020198754). Total 6 databases (PubMed/Medline, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL, ProQuest, and Cochrane) were searched. Among 1734 records, only four randomized controlled trials were included. The review included a total of 203 participants (103 in the intervention group and 100 in the control/standard group) with type 2 diabetic nephropathy or stage 2,3, or 4 of chronic kidney disease. The meta-analysis showed no effects of exercise on serum creatinine, serum cystatin c and varied eGFR equations. However, exercise decreased urinary albumin to creatinine ratio, urinary protein to creatinine ratio, serum urea nitrogen, creatinine clearance, and urinary protein excretion while increasing urea clearance. Limited evidence on the reno-protective role of exercise demands future research in this direction.
أهداف البحث: يسبب اعتلال الكلية السكري مضاعفات في القلب والأوعية الدموية لدى الأفراد المصابين بداء السكري، مما يؤدي إلى انخفاض وظائف الكلى والتدهور الجسدي العام. كان الهدف من هذه المراجعة المنهجية هو تحديد تأثير التمرين على متغيرات وظائف الكلى المختلفة بين الأفراد المصابين بداء السكري من النوع الثاني واعتلال الكلية.
طرق البحث: تم تسجيل المراجعة المنهجية في قاعدة بيانات "بروسبيرو"، وتم البحث في قواعد البيانات التالية: ميدلاين، وسكوبس، وشبكة العلوم، وسيناهل، وبروكويست، وكوكران. من بين 1734 سجل وجدت فقط أربع تجارب معشاة ذات شواهد، وتم تضمينها في التوليف النوعي والكمي بعد فحص أهلية الدراسة في مرحلة العنوان والملخص والنص الكامل.
النتائج: تضمنت المراجعة ما مجموعه 203 شخصا (103 في مجموعة التدخل و 100 في المجموعة الضابطة / القياسية) مصابين باعتلال الكلية السكري من النوع 2 أو مرض الكلى المزمن في المراحل 2 و 3 و 4. استخدمت ثلاث من الدراسات الأربع مبدأ "فيت" (التكرار، والشدة، والوقت، والنوع) في تدريب التمرينات والوصفات الطبية. تلقت مجموعة التدخل تمارين هوائية ومقاومة، منزلية، خاضعة للإشراف، ومنظمة. أظهر التحليل التلوي عدم وجود تأثير للتمرين على كرياتينين المصل، وسيستاتين المصل، ومعادلة الكرياتينين، ومعادلة سيستاتين، ومعادلة الكرياتينين-سيستاتين. ومع ذلك ، فقد أدت التمارين الرياضية إلى خفض نسبة الألبومين البولي إلى نسبة الكرياتينين، ونسبة البروتين البولي إلى نسبة الكرياتينين، ونتروجين اليوريا في الدم، وإزالة الكرياتينين، وإفراز البروتين في البول مع زيادة تصفية اليوريا.
الاستنتاجات: هناك دليل محدودة على دور التمارين في وقاية الكلى وتغيير معايير وظائف الكلى بين مرضى السكري من النوع الثاني المصابين باعتلال الكلية.
Keywords: CI, confidence interval; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetes mellitus; Diabetic kidney disease; Exercise; Kidney function; Nephropathy; RCT, randomized controlled trial; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
© 2022 [The Author/The Authors].
Figures






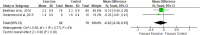
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of statins in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Oct 12;15(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0350-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27733168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of physical activity on the progression of diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jan 29;41(1):BSR20203624. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203624. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33289502 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary polyphenols in the glycemic, renal, inflammatory, and oxidative stress biomarkers in diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Rev. 2022 Nov 7;80(12):2237-2259. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuac035. Nutr Rev. 2022. PMID: 35595310
-
Efficacy and safety of Shenkang injection as adjuvant therapy in patients with diabetic nephropathy: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 24;99(52):e23821. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023821. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33350769 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation at estimating glomerular filtration rate in adults with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol.BMJ Open. 2019 Aug 30;9(8):e031558. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031558. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31473625 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diabetic kidney disease and cardiac autonomic neuropathy: insights on exercise rehabilitation.J Nephrol. 2025 Mar;38(2):457-471. doi: 10.1007/s40620-025-02216-6. Epub 2025 Feb 6. J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39909963 Review.
-
Comparison of the effect of aerobic and resistance training on fatigue, quality of life and biochemical factors in hemodialysis patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 24;15(1):10052. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94257-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40122960 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Physiotherapeutic Approach for Paraparesis Resulting From L2-S1 Disc Bulge Along With Diabetic Neuropathy: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Jan 10;16(1):e52056. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52056. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38344621 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Medicine in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Utility and Limitations.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Nov 16;16:3669-3689. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S390752. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 38028995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of exercise-based rehabilitation on functional capacity and renal function in type 2 diabetes mellitus with nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Aug;56(8):2671-2682. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-03987-w. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38483735 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- diabetes A. Idf.org; 2020. International diabetes federation - complications [Internet]https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/complications.html [cited 22 January 2020]. Available from.
-
- Greenberg A. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2009. Primer on kidney diseases E-book.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

