Angiopoietin-1 derived peptide hydrogel promotes molecular hallmarks of regeneration and wound healing in dermal fibroblasts
- PMID: 36818306
- PMCID: PMC9932487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.105984
Angiopoietin-1 derived peptide hydrogel promotes molecular hallmarks of regeneration and wound healing in dermal fibroblasts
Abstract
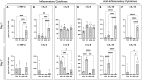
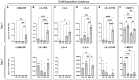
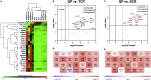
By providing an ideal environment for healing, biomaterials can be designed to facilitate and encourage wound regeneration. As the wound healing process is complex, there needs to be consideration for the cell types playing major roles, such as fibroblasts. As a major cell type in the dermis, fibroblasts have a large impact on the processes and outcomes of wound healing. Prevopisly, conjugating the angiopoietin-1 derived Q-peptide (QHREDGS) to a collagen-chitosan hydrogel created a biomaterial with in vivo success in accelerating wound healing. This study utilized solvent cast Q-peptide conjugated collagen-chitosan seeded with fibroblast monolayers to investigate the direct impact of the material on this major cell type. After 24 h, fibroblasts had a significant change in release of anti-inflammatory, pro-healing, and ECM deposition cytokines, with demonstrated immunomodulatory effects on macrophages and upregulated expression of critical wound healing genes.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Health sciences; Materials science.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.R. is a founder of Quthero Inc, holds equity in the company, receives consulting fees from the company and is a member of its Board of Directors. S.M. holds equity in Quthero Inc. M.R. and S.M. are inventors of patents licensed by Quthero Inc and they receive royalty payments from those patents.
Figures

References
-
- Sullivan V.J., Myers S. Plastic Surgery - Principles and Practice. Elsevier; 2022. Skin structure and function, wound healing and scarring; pp. 1–14. - DOI
-
- Fife C.E., Carter M.J., Walker D., Thomson B. Wound care outcomes and associated cost among patients treated in US outpatient wound centers: data from the US wound registry. Wounds. 2012;24:10–17. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

