Benign lymphoepithelial cyst of parotid gland without human immunodeficiency virus infection: A case report
- PMID: 36818610
- PMCID: PMC9928695
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i4.931
Benign lymphoepithelial cyst of parotid gland without human immunodeficiency virus infection: A case report
Abstract
Background: Benign lymphoepithelial cyst (BLEC) of the parotid gland is a rare benign embryonic-dysplastic cystic tumor in the anterolateral neck that occurs most commonly in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive adults and rarely in non-acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. The main presentation is a slow-growing, painless mass, and secondary infection may cause acute inflammatory symptoms.
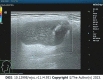
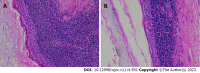
Case summary: A 44-year-old Chinese male patient presented with a 1-year history of a mass in the left side of the neck. On physical examination, a mass similar in size and shape to a quail egg was found in the left parotid gland. The mass was tough, without tenderness, and easily moveable. The results of HIV tests, including antibody and nucleic acid tests and CD4+ T cell examination, were negative. Imaging examination revealed a left parotid gland mass. The patient underwent surgical treatment, and BLEC was diagnosed based on postoperative pathology. After 2 years of follow-up, the patient survived well without related discomfort.
Conclusion: The detailed characteristics of a BLEC in a patient without HIV infection contribute to an improved understanding of this rare disease.
Keywords: Benign lymphoepithelial cyst; Case report; Human immunodeficiency virus; Parotid gland.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Branchial cleft cyst in the parotid gland in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient.Arch Craniofac Surg. 2019 Jun;20(3):191-194. doi: 10.7181/acfs.2019.00031. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31256557 Free PMC article.
-
The benign lymphoepithelial cyst and a classification system for lymphocytic parotid gland enlargement in the pediatric HIV population.Laryngoscope. 2007 Jan;117(1):106-13. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000246196.35413.35. Laryngoscope. 2007. PMID: 17202938 Review.
-
Benign Lymphoepithelial Cyst: An Unusual Cause of Parotid Swelling in Two Immunocompetent Patients.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Jul 14;7(13):2142-2145. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.577. eCollection 2019 Jul 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31456841 Free PMC article.
-
Benign Lymphoepithelial Cyst of Parotid Gland: A Pathologist's Perspective.J Cytol. 2023 Oct-Dec;40(4):217-219. doi: 10.4103/joc.joc_61_23. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Cytol. 2023. PMID: 38058667 Free PMC article.
-
Parotid lymphoepithelial cysts in human immunodeficiency virus: a review.J Laryngol Otol. 2013 Nov;127(11):1046-9. doi: 10.1017/S0022215113002417. Epub 2013 Oct 29. J Laryngol Otol. 2013. PMID: 24169222 Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating Parotid Lymphoepithelial Cysts in HIV Patients: A Tale of Two Distinct Scenarios.Cureus. 2023 Dec 12;15(12):e50399. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50399. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38213382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dave SP, Pernas FG, Roy S. The benign lymphoepithelial cyst and a classification system for lymphocytic parotid gland enlargement in the pediatric HIV population. Laryngoscope. 2007;117:106–113. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

