Synthetic MRI, multiplexed sensitivity encoding, and BI-RADS for benign and malignant breast cancer discrimination
- PMID: 36818669
- PMCID: PMC9936239
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1080580
Synthetic MRI, multiplexed sensitivity encoding, and BI-RADS for benign and malignant breast cancer discrimination
Abstract
Objective: To assess the diagnostic value of predictive models based on synthetic magnetic resonance imaging (syMRI), multiplexed sensitivity encoding (MUSE) sequences, and Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions.
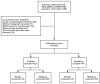
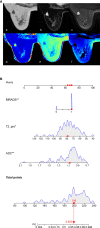
Methods: Clinical and MRI data of 158 patients with breast lesions who underwent dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), syMRI, and MUSE sequences between September 2019 and December 2020 were retrospectively collected. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of MUSE and quantitative relaxation parameters (longitudinal and transverse relaxation times [T1, T2], and proton density [PD] values) of syMRI were measured, and the parameter variation values and change in their ratios were calculated. The patients were randomly divided into training (n = 111) and validation (n = 47) groups at a ratio of 7:3. A nomogram was built based on univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses in the training group and was verified in the validation group. The discriminatory and predictive capacities of the nomogram were assessed by the receiver operating characteristic curve and area under the curve (AUC). The AUC was compared by DeLong test.
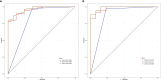
Results: In the training group, univariate analysis showed that age, lesion diameter, menopausal status, ADC, T2pre, PDpre, PDGd, T2Delta, and T2ratio were significantly different between benign and malignant breast lesions (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that ADC and T2pre were significant variables (all P < 0.05) in breast cancer diagnosis. The quantitative model (model A: ADC, T2pre), BI-RADS model (model B), and multi-parameter model (model C: ADC, T2pre, BI-RADS) were established by combining the above independent variables, among which model C had the highest diagnostic performance, with AUC of 0.965 and 0.986 in the training and validation groups, respectively.
Conclusions: The prediction model established based on syMRI, MUSE sequence, and BI-RADS is helpful for clinical differentiation of breast tumors and provides more accurate information for individualized diagnosis.
Keywords: breast cancer; diffusion-weighted imaging; multiplexed sensitivity-encoding; nomogram; synthetic magnetic resonance imaging (syMRI).
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Xu, Ren, Li, Xi and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors JR, ZL, and LX were employed by GE Healthcare. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The value of synthetic MRI in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2021 Aug 23;43(8):872-877. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20210322-00254. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34407594 Chinese.
-
A nomogram based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging improves the diagnostic performance of breast lesions diagnosed as BI-RADS category 4: A comparative study with the Kaiser score.Eur J Radiol. 2025 Feb;183:111920. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2025.111920. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Eur J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39793481
-
Multiparameter MRI Model With DCE-MRI, DWI, and Synthetic MRI Improves the Diagnostic Performance of BI-RADS 4 Lesions.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 15;11:699127. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.699127. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34722246 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI model with synthetic MRI, DWI multi-quantitative parameters, and differential sub-sampling with cartesian ordering enables BI-RADS 4 lesions diagnosis with high accuracy.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 5;13:1180131. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1180131. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38250550 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Synthetic Relaxometry and Diffusion Measures in the Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions as Compared to BI-RADS.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Apr;53(4):1118-1127. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27435. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33179809
Cited by
-
Quantitative characterization of breast lesions and normal fibroglandular tissue using compartmentalized diffusion-weighted model: comparison of intravoxel incoherent motion and restriction spectrum imaging.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 24;26(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01828-3. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38658999 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factor analysis of conversion in laparoscopic liver resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Surg Endosc. 2024 Mar;38(3):1191-1199. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10579-9. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38082010
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

