Genomic identification of cotton SAC genes branded ovule and stress-related key genes in Gossypium hirsutum
- PMID: 36818879
- PMCID: PMC9935941
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1123745
Genomic identification of cotton SAC genes branded ovule and stress-related key genes in Gossypium hirsutum
Abstract
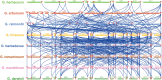
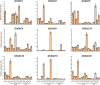
SAC genes have been identified to play a variety of biological functions and responses to various stresses. Previously, SAC genes have been recognized in animals and Arabidopsis. For the very first time, we identified 157 SAC genes in eight cotton species including three diploids and five tetraploids with 23 SAC members in G. hirsutum. Evolutionary analysis classified all cotton SAC gene family members into five distinct groups. Cotton SAC genes showed conserved sequence logos and WGD or segmental duplication. Multiple synteny and collinearity analyses revealed gene family expansion and purifying selection pressure during evolution. G. hirsutum SAC genes showed uneven chromosomal distribution, multiple exons/introns, conserved protein motifs, and various growth and stress-related cis-elements. Expression pattern analysis revealed three GhSAC genes (GhSAC3, GhSAC14, and GhSAC20) preferentially expressed in flower, five genes (GhSAC1, GhSAC6, GhSAC9, GhSAC13, and GhSAC18) preferentially expressed in ovule and one gene (GhSAC5) preferentially expressed in fiber. Similarly, abiotic stress treatment verified that GhSAC5 was downregulated under all stresses, GhSAC6 and GhSAC9 were upregulated under NaCl treatment, and GhSAC9 and GhSAC18 were upregulated under PEG and heat treatment respectively. Overall, this study identified key genes related to flower, ovule, and fiber development and important genetic material for breeding cotton under abiotic stress conditions.
Keywords: SAC genes; abiotic stresses; cotton; flower; multiple synteny; ovule; phylogenetic analysis.
Copyright © 2023 Shuya, Le, Huiyun, Yu, Yujun and Qanmber.
Conflict of interest statement
The AE MA declared a shared affiliation with the Authors MS, LL, SH at the time of review. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genomic insights into CKX genes: key players in cotton fibre development and abiotic stress responses.PeerJ. 2024 May 30;12:e17462. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17462. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38827302 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Histone H3 (HH3) Genes in Gossypium hirsutum Revealed Diverse Expression During Ovule Development and Stress Responses.Genes (Basel). 2019 May 9;10(5):355. doi: 10.3390/genes10050355. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31075950 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide identification, classification and functional characterization of heat shock transcription factors in cultivated and ancestral cottons (Gossypium spp.).Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jul 1;182:1507-1527. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.016. Epub 2021 May 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33965497
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase genes in cotton (Gossypium spp.) in plant development and abiotic stresses.BMC Genomics. 2020 Aug 15;21(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06970-8. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32799801 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of floral morphoanatomy and identification of marker genes preferentially expressed during specific stages of cotton flower development.Planta. 2020 Oct 1;252(4):71. doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03477-0. Planta. 2020. PMID: 33001252
Cited by
-
Decoding drought resilience: a comprehensive exploration of the cotton Eceriferum (CER) gene family and its role in stress adaptation.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 29;24(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05172-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38811873 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic insights into CKX genes: key players in cotton fibre development and abiotic stress responses.PeerJ. 2024 May 30;12:e17462. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17462. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38827302 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide and Expression Pattern Analysis of the DVL Gene Family Reveals GhM_A05G1032 Is Involved in Fuzz Development in G. hirsutum.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):1346. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021346. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali F., Qanmber G., Wei Z., Yu D., Li Y., Gan L., et al. . (2020). Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of geranyl geranyl diphosphate synthase genes of cotton (Gossypium spp.) in plant development and abiotic stresses. BMC Genomics 21:1–15. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06970-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

