Emerging technologies for COVID (ET-CoV) detection and diagnosis: Recent advancements, applications, challenges, and future perspectives
- PMID: 36818992
- PMCID: PMC9917176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104642
Emerging technologies for COVID (ET-CoV) detection and diagnosis: Recent advancements, applications, challenges, and future perspectives
Abstract
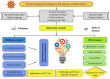
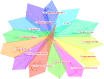
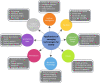
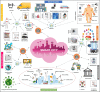
In light of the constantly changing terrain of the COVID outbreak, medical specialists have implemented proactive schemes for vaccine production. Despite the remarkable COVID-19 vaccine development, the virus has mutated into new variants, including delta and omicron. Currently, the situation is critical in many parts of the world, and precautions are being taken to stop the virus from spreading and mutating. Early identification and diagnosis of COVID-19 are the main challenges faced by emerging technologies during the outbreak. In these circumstances, emerging technologies to tackle Coronavirus have proven magnificent. Artificial intelligence (AI), big data, the internet of medical things (IoMT), robotics, blockchain technology, telemedicine, smart applications, and additive manufacturing are suspicious for detecting, classifying, monitoring, and locating COVID-19. Henceforth, this research aims to glance at these COVID-19 defeating technologies by focusing on their strengths and limitations. A CiteSpace-based bibliometric analysis of the emerging technology was established. The most impactful keywords and the ongoing research frontiers were compiled. Emerging technologies were unstable due to data inconsistency, redundant and noisy datasets, and the inability to aggregate the data due to disparate data formats. Moreover, the privacy and confidentiality of patient medical records are not guaranteed. Hence, Significant data analysis is required to develop an intelligent computational model for effective and quick clinical diagnosis of COVID-19. Remarkably, this article outlines how emerging technology has been used to counteract the virus disaster and offers ongoing research frontiers, directing readers to concentrate on the real challenges and thus facilitating additional explorations to amplify emerging technologies.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; CiteSpace; Detection; Emerging technologies; Network visualization; SARS-COVID-2.
© 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures










Similar articles
-
A critical review of emerging technologies for tackling COVID-19 pandemic.Hum Behav Emerg Technol. 2021 Jan;3(1):25-39. doi: 10.1002/hbe2.237. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Hum Behav Emerg Technol. 2021. PMID: 33363278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Technological Solutions to Analyse the Effects of Pandemic Outbreak on Human Lives.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Feb 18;58(2):311. doi: 10.3390/medicina58020311. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35208634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blockchain and AI-Based Solutions to Combat Coronavirus (COVID-19)-Like Epidemics: A Survey.IEEE Access. 2021 Jun 30;9:95730-95753. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3093633. eCollection 2021. IEEE Access. 2021. PMID: 34812398 Free PMC article.
-
Federated Learning and Internet of Medical Things - Opportunities and Challenges.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2022 Jun 29;295:201-204. doi: 10.3233/SHTI220697. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2022. PMID: 35773843
-
An architecture for COVID-19 analysis and detection using big data, AI, and data architectures.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 1;19(8):e0305483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305483. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39088543 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synergizing Intelligence and Building a Smarter Future: Artificial Intelligence Meets Bioengineering.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;10(6):691. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10060691. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370622 Free PMC article.
-
Automated machine learning for the identification of asymptomatic COVID-19 carriers based on chest CT images.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Feb 27;24(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01211-w. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38413923 Free PMC article.
-
Binary Classification of Pneumonia in Chest X-Ray Images Using Modified Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization Algorithm.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;25(13):3976. doi: 10.3390/s25133976. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tian B., Gao F., Fock J., Dufva M., Hansen M.F. Homogeneous circle-to-circle amplification for real-time optomagnetic detection of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp coding sequence. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020;165 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
