Bio-inspired neural networks for decision-making mechanisms and neuromodulation for motor control in a differential robot
- PMID: 36819006
- PMCID: PMC9936153
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbot.2023.1078074
Bio-inspired neural networks for decision-making mechanisms and neuromodulation for motor control in a differential robot
Abstract
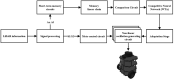
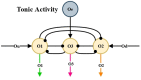
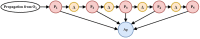
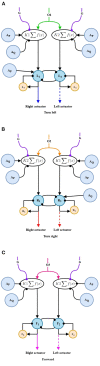
The aim of this work is to propose bio-inspired neural networks for decision-making mechanisms and modulation of motor control of an automaton. In this work, we have adapted and applied cortical synaptic circuits, such as short-term memory circuits, winner-take-all (WTA) class competitive neural networks, modulation neural networks, and nonlinear oscillation circuits, in order to make the automaton able to avoid obstacles and explore simulated and real environments. The performance achieved by using biologically inspired neural networks to solve the task at hand is similar to that of several works mentioned in the specialized literature. Furthermore, this work contributed to bridging the fields of computational neuroscience and robotics.
Keywords: adaptation stage; automaton; bio-inspired neural network; differential robot; exploration behavior; neuromodulation network; signal processing.
Copyright © 2023 Guerrero-Criollo, Castaño-López, Hurtado-López and Ramirez-Moreno.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Ring attractor bio-inspired neural network for social robot navigation.Front Neurorobot. 2023 Aug 31;17:1211570. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2023.1211570. eCollection 2023. Front Neurorobot. 2023. PMID: 37719331 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic plasticity in a recurrent neural network for versatile and adaptive behaviors of a walking robot.Front Neurorobot. 2015 Oct 13;9:11. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2015.00011. eCollection 2015. Front Neurorobot. 2015. PMID: 26528176 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic analysis of a general class of winner-take-all competitive neural networks.IEEE Trans Neural Netw. 2010 May;21(5):771-83. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2041671. Epub 2010 Mar 8. IEEE Trans Neural Netw. 2010. PMID: 20215068
-
Advances in Zeroing Neural Networks: Bio-Inspired Structures, Performance Enhancements, and Applications.Biomimetics (Basel). 2025 Apr 29;10(5):279. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics10050279. Biomimetics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An efficient neural network approach to dynamic robot motion planning.Neural Netw. 2000 Mar;13(2):143-8. doi: 10.1016/s0893-6080(99)00103-3. Neural Netw. 2000. PMID: 10935758 Review.
Cited by
-
Ring attractor bio-inspired neural network for social robot navigation.Front Neurorobot. 2023 Aug 31;17:1211570. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2023.1211570. eCollection 2023. Front Neurorobot. 2023. PMID: 37719331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao Z., Cheng L., Zhou C., Gu N., Wang X., Tan M. (2015). Spiking neural network-based target tracking control for autonomous mobile robots. Neural Comput. Appl. 26, 1839–1847. 10.1007/s00521-015-1848-5 - DOI
-
- Foundation O. S. R. (2014). Gazebo. Available online at: http://gazebosim.org/
-
- Guerrero-Criollo R. J., Castaño-López J. A., Díaz-Cuchala R. E., David Rozo-Giraldo Y., Ramirez-Moreno D. F. (2022). Design and simulation of a bio-inspired neural network for the motor control of a mobile automaton, in 2022 IEEE Colombian Conference on Applications of Computational Intelligence (ColCACI) (Cali: IEEE; ), 1–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

