Pseudorabies virus exploits N6-methyladenosine modification to promote viral replication
- PMID: 36819040
- PMCID: PMC9936159
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1087484
Pseudorabies virus exploits N6-methyladenosine modification to promote viral replication
Abstract
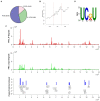
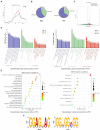
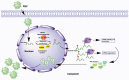
Introduction: Pseudorabies virus (PRV) is the pathogenic virus of porcine pseudorabies (PR), belonging to the Herpesviridae family. PRV has a wide range of hosts and in recent years has also been reported to infect humans. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is the major pathway of RNA post-transcriptional modification. Whether m6A modification participates in the regulation of PRV replication is unknown.
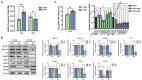
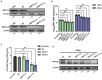
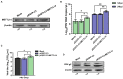
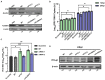
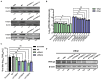
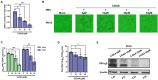
Methods: Here, we investigated that the m6A modification was abundant in the PRV transcripts and PRV infection affected the epitranscriptome of host cells. Knockdown of cellular m6A methyltransferases METTL3 and METTL14 and the specific binding proteins YTHDF2 and YTHDF3 inhibited PRV replication, while silencing of demethylase ALKBH5 promoted PRV output. The overexpression of METTL14 induced more efficient virus proliferation in PRV-infected PK15 cells. Inhibition of m6A modification by 3-deazaadenosine (3-DAA), a m6A modification inhibitor, could significantly reduce viral replication.
Results and discussion: Taken together, m6A modification played a positive role in the regulation of PRV replication and gene expression. Our research revealed m6A modification sites in PRV transcripts and determined that m6A modification dynamically mediated the interaction between PRV and host.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; m6A regulators; pseudorabies virus; regulation; replication.
Copyright © 2023 Yu, Wu, Cao, Wen, Huang, Zhao, Lang, Zhao, Lin, Du, Yu and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

