ECG Changes in a Patient Presenting With Chest Pain Secondary to Left-Sided Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Case Report-Based Literature Review
- PMID: 36819410
- PMCID: PMC9936199
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33904
ECG Changes in a Patient Presenting With Chest Pain Secondary to Left-Sided Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Case Report-Based Literature Review
Abstract
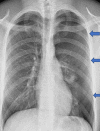
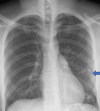
Pneumothorax is the accumulation of air in the extrapulmonary space between the pleura and the chest wall. Spontaneous pneumothorax can present with various electrocardiographic (ECG) findings including axis deviation, bundle branch block and T waves inversion. A 23-year-old young male patient of slim build presented to the accident and emergency department with sudden-onset chest pain and shortness of breath. He had pleuritic chest pain, worse on breathing. Electrocardiogram showed right axis deviation, diminished or low-amplitude R waves and small-amplitude QRS complexes in the precordial leads. Vital signs were stable and physical examination showed reduced air entry on the left side. Chest radiography showed significant left-sided pneumothorax and the patient had an emergency chest drain inserted. ECG changes resolved with the resolution of pneumothorax. He was discharged home after four days of hospital admission and complete resolution of pneumothorax.
Keywords: chest pain in the young; chest tube; chest xray cx-ray; electrocardiogram (ecg/ekg); emergency chest drain; primary pneumothorax; right axis deviation; shortness of breath (sob).
Copyright © 2023, Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electrocardiographic manifestations in a large right-sided pneumothorax.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Mar 23;21(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01470-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 33757495 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: an electrocardiogram of spontaneous pneumothorax mimicking arm lead reversal.J Emerg Med. 2014 May;46(5):620-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.09.016. Epub 2014 Jan 17. J Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 24440619
-
Acute right bundle branch block due to pneumothorax.J Family Med Prim Care. 2018 Sep-Oct;7(5):1126-1128. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_222_18. J Family Med Prim Care. 2018. PMID: 30598975 Free PMC article.
-
Left spontaneous pneumothorax presenting with ST-segment elevations: a case report and review of the literature.Heart Lung. 2011 Jan-Feb;40(1):88-91. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2010.09.007. Heart Lung. 2011. PMID: 21320674 Review.
-
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax during pregnancy: A case report and review of the literature.Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim (Engl Ed). 2022 Oct;69(8):506-509. doi: 10.1016/j.redare.2021.03.020. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim (Engl Ed). 2022. PMID: 36085144 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrocardiographic changes in pneumothorax: an updated review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Apr 19;86(6):3551-3556. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002080. eCollection 2024 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38846885 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Case report: an electrocardiogram of spontaneous pneumothorax mimicking arm lead reversal. Wieters JS, Carlin JP, Morris A. J Emerg Med. 2014;46:620–623. - PubMed
-
- Electrocardiographic changes in patients with spontaneous pneumothorax. Krenke R, Nasilowski J, Przybylowski T, Chazan R. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19218660/ J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;59 Suppl 6:361–373. - PubMed
-
- ECG changes in pneumothorax patients presenting to the emergency department. Karakoyun S, Boran M, Boran E, Saritas A. Turk Thorac J. 2019;20:155.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
