SOCS3 protein expression predicts the responses of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients to platinum-based chemotherapy
- PMID: 36819530
- PMCID: PMC9929795
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-6065
SOCS3 protein expression predicts the responses of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients to platinum-based chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: This study sought to assess the relationship between suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) expression, SOCS3 promoter methylation status, and platinum-based chemotherapy responses in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
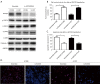
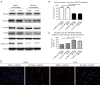
Methods: A total of 400 advanced NSCLC patients with inoperable disease were enrolled in this study. All the patients underwent platinum-based chemotherapy treatment, and the clinical and prognostic outcomes of these patients were analyzed. The SOCS3 protein expression and SOCS3 promoter methylation status of the tumor tissues in these patients were also tested by immunohistochemistry and polymerase chain reaction (PCR), respectively. In addition, we knocked down SOCS3 expression via small-interfering RNA (siRNA) in the lung cancer cell lines and conducted in vitro analyses to examine cell viability and apoptosis.
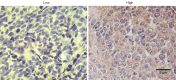
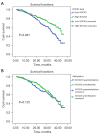
Results: Patients with higher expression levels of SOCS3 were found to have a lower average tumor stage, higher average tumor differentiation, and higher rates of positive chemotherapy responses than those with lower expression levels of SOCS3. SOCS3 promoter methylation was also found to be correlated with chemotherapy responses in these patients. In the prognostic analyses, only SOCS3 expression, but not SOCS3 promoter methylation, was found to be predictive of outcomes in advanced NSCLC patients. We also found that the pro-apoptotic effects of SOCS3 were mediated by the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathways in the lung cancer cells.
Conclusions: Currently, there is a lack of reliable biomarkers for predicting the responses of NSCLC patients to chemotherapy. Our results may aid in clinical evaluations of NSCLC patients.
Keywords: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3); non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); promoter methylation; treatment response.
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-6065/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
