Subglottic Masses Revealing Rosai-Dorfman Disease
- PMID: 36819645
- PMCID: PMC9930883
- DOI: 10.12890/2023_003389
Subglottic Masses Revealing Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Abstract
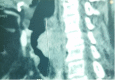
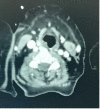
Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) is an uncommon lymphoproliferative disorder; RDD with oropharyngeal involvement is extremely rare, especially in adults. A 65-year-old woman with a complaint of progressive dyspnoea since 2016 presented with laryngeal involvement of RDD. A laryngoscopy examination revealed two solid, polypoid masses in the subglottic region, and a laryngeal biopsy concluded chronic inflammation without signs of malignancy. A second biopsy of axillary lymph nodes was performed, supporting the diagnosis of histiocytosis. The patient was treated with corticosteroids and then lost to follow-up. In 2019, she suffered from dyspnoea and a hoarse voice. Laryngoscopy examination showed a polypoid lesion causing airway obstruction at 70% and thickening of the lateral wall of the cavum. Physical examination found left axillary and submandibular adenopathy, and computed tomography revealed thickening of the supraglottic larynx narrowing the laryngeal pathway. Lymphadenectomy with immunohistochemical analysis revealed typical protein positive S-100 histiocytes and emperipolesis. The patient was treated with high doses of corticosteroids for six weeks then these were progressively decreased. The outcome was favourable; the laryngeal lesion disappeared after two weeks of treatment.
Learning points: Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare cause of lymphadenopathy in adults. Extranodal presentation of the disease is possible mainly in the head and the neck region.The diagnosis is based on histological examination with the presence of histiocytes, which are S-100 positive, CD68 positive, and CD1a negative immunohistochemistry.The outcome is usually good in asymptomatic forms of the disease with no critical organ involved. The surgical resection is appropriate to the localised symptomatic form of the disease while corticosteroids are indicated in disseminated RDD as a first-line therapy.Inspired by our case, rare localisation of Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD), led to clinical and therapeutic issues. That is why a review of the literature must be undertaken, to share experiences.
Keywords: Rosai Dofmann disease; laryngeal involvement; steroids.
© EFIM 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7(1):19–73. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter RJ, 3rd, Banks PM, McDonald TJ, Sanderson DR. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): report of a case with respiratory tract involvement. Laryngoscope. 1978;88(12):1963–9. - PubMed
-
- Aluffi P, Prestinari A, Ramponi A, Castri M, Pia F. Rosai-Dorfman disease of the larynx. J Laryngol Otol. 2000;114(7):565–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources