The Effect of N6-Methyladenosine Regulators and m6A Reader YTHDC1-Mediated N6-Methyladenosine Modification Is Involved in Oxidative Stress in Human Aortic Dissection
- PMID: 36819785
- PMCID: PMC9935809
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/3918393
The Effect of N6-Methyladenosine Regulators and m6A Reader YTHDC1-Mediated N6-Methyladenosine Modification Is Involved in Oxidative Stress in Human Aortic Dissection
Abstract
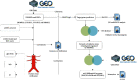
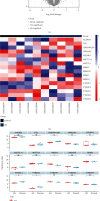
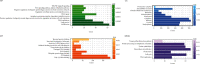
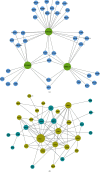
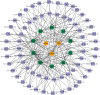
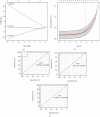
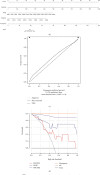
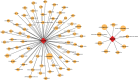
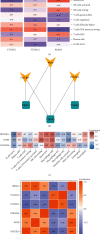
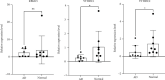
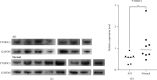
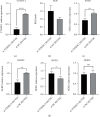
Aortic dissection (AD) develops pathological changes in the separation of the true and false aortic lumen, with high lethality. m6A methylation and oxidative stress have also been shown to be involved in the onset of AD. Through bioinformatics methods, three differentially expressed m6A regulators (YTHDC1, YTHDC2, and RBM15) were excavated from the GSE52093 dataset in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, and functional enrichment analysis of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) regulated by m6A regulators was performed. Then, the genes with oxidative stress-related functions among these genes were found. The protein interaction network of the oxidative stress-related genes and the competing endogenous RNA- (ceRNA-) miRNA-mRNA network were constructed. Among them, DHCR24, P4HB, and PDGFRA, which have m6A differences in AD samples, were selected as key genes. We also performed immune infiltration analysis, as well as cell-gene correlation analysis, on samples from the dataset. The results showed that YTHDC1 was positively correlated with macrophage M1 and negatively correlated with macrophage M2. Finally, we extracted AD and healthy aorta RNA and protein from human tissues that were taken from AD patients and patients who received heart transplants, performed quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) on YTHDC2 and RBM15, and performed qRT-PCR and western blot (WB) detection on YTHDC1 to verify their differences in AD. The mRNA and protein levels of YTHDC1 were consistent with the results of bioinformatics analysis and were downregulated in AD. Immunofluorescence (IF) was used to colocalize YTHDC1 and endothelial cell marker CD31. After knocking down YTHDC1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels had a tendency to increase and the expression of peroxide dismutase SOD2 was decreased. This study provides assistance in discovering the role of m6A regulator YTHDC1 in AD. In particular, m6A modification participates in oxidative stress and jointly affects AD.
Copyright © 2023 Fanxing Yin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelial downregulation of nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 promotes pulmonary vascular remodeling in sugen hypoxia model of pulmonary hypertension.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 23;10(3):e24963. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24963. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38318069 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in primary Sjögren's syndrome.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 16;9:959388. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.959388. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36465909 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental validation and comprehensive analysis of m6A methylation regulators in intervertebral disc degeneration subpopulation classification.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 10;14(1):8417. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58888-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38600232 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in Cancer progression.Mol Cancer. 2020 May 12;19(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01204-7. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32398132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Feb 21;6(1):74. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00450-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33611339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the relationship between single-cell N6-methyladenosine regulators and the infiltrating immune cells in esophageal carcinoma.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 13;9(8):e18132. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18132. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37529341 Free PMC article.
-
Role of N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase component RBM15 in cancer progression and its therapeutic potential.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 22;16(1):855. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02644-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40402374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a 6-gene signature derived from RNA modification-associated genes for the diagnosis of Acute Stanford Type A Aortic Dissection.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2024 Sep 28;21(9):884-898. doi: 10.26599/1671-5411.2024.09.007. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39483269 Free PMC article.
-
WTAP and m6A-modified circRNAs modulation during stress response in acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jun 23;81(1):276. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05299-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38909325 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in inflammation: a bibliometric analysis and literature review.PeerJ. 2024 Dec 13;12:e18645. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18645. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39686999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

