Predicting the Classification of Home Oxygen Therapy for Post-COVID-19 Rehabilitation Patients Using a Neural Network
- PMID: 36819912
- PMCID: PMC9910350
- DOI: 10.1298/ptr.E10181
Predicting the Classification of Home Oxygen Therapy for Post-COVID-19 Rehabilitation Patients Using a Neural Network
Abstract
Objective: We evaluated the accuracy of a neural network to classify and predict the possibility of home oxygen therapy at the time of discharge from hospital based on patient information post-coronavirus disease (COVID-19) at admission.
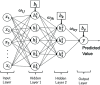
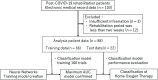
Methods: Patients who survived acute treatment with COVID-19 and were admitted to the Amagasaki Medical Co-operative Hospital during August 2020-December 2021 were included. However, only rehabilitation patients (n = 88) who were discharged after a rehabilitation period of at least 2 weeks and not via home or institution were included. The neural network model implemented in R for Windows (4.1.2) was trained using data on patient age, gender, and number of days between a positive polymerase chain reaction test and hospitalization, length of hospital stay, oxygen flow rate required at hospitalization, and ability to perform activities of daily living. The number of training trials was 100. We used the area under the curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity as evaluation indicators for the classification model.
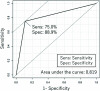
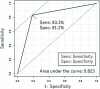
Results: The model of states at rest had as AUC of 0.82, sensitivity of 75.0%, specificity of 88.9%, and model accuracy of 86.4%. The model of states on exertion had an ACU of 0.82, sensitivity of 83.3%, specificity of 81.3%, and model accuracy of 81.8%.
Conclusion: The accuracy of this study's neural network model is comparable to that of previous studies recommended by Japanese Guidelines for the Physical Therapy and is expected to be used in clinical practice. In future, it could be used as a more accurate clinical support tool by increasing the sample size and applying cross-validation.
Keywords: COVID-19; Classification; Home oxygen therapy; Machine learning; Neural network.
©2022 Japanese Society of Physical Therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Comparison of the predictive performance of Logistic regression, BP neural network and support vector machine model for the risk of acute exacerbation of readmission in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease within 30 days].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Aug;34(8):819-824. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220303-00198. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 36177924 Chinese.
-
Therapeutic respiratory and functional rehabilitation protocol for intensive care unit patients affected by COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Apr 12;22(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05210-y. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33845878 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 16;3:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub4. PMID: 33242342 Updated.
-
Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 14;5(5):CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 10;7:CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub2. PMID: 32406927 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- World Health Organization [Internet] . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard [cited 2022 Jan 1]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare [Internet] . Trends in national outbreaks of new coronavirus infections [cited 2022 Jan 1]. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10906000/000871839.pdf (in Japanese)
-
- Sun T, Guo L, et al. : Rehabilitation of patients with COVID-19. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020; 14: 1249–1256. - PubMed

