Smart product-service systems in the healthcare industry: Intelligent connected products and stakeholder communication drive digital health service adoption
- PMID: 36820023
- PMCID: PMC9937901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13137
Smart product-service systems in the healthcare industry: Intelligent connected products and stakeholder communication drive digital health service adoption
Abstract
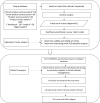
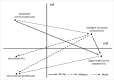
Smart product-service systems (PSSs) have emerged as a solution for the ongoing digitalization of products and services, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic and under social distancing. However, the conditions for smart PSS adoption remain unclear, requiring the identification of driving attributes and the interrelationships of the attributes for smart PSS implementation in the healthcare industry. This study contributes by determining the cause-effect interrelationship among smart PSS attributes and by identifying and prioritizing the criteria that drive smart PSS adoption in chronic disease management. The study constructed a five-aspect theoretical model to deepen the understanding of digital health service adoption drivers. Data were collected from 233 healthcare industry practitioners to validate the smart PSS adoption attributes. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) determined the structure of the attributes, the reliability of the criteria, and the validity of the aspects. The EFA result suggested 24 valid and reliable criteria drivers of smart PSS adoption in the healthcare industry, and they were grouped into five aspects. Following the smart PSS literature and stakeholder theory, the aspects are named digital health service adoption, intelligent connected products, stakeholder communication, environmental benefits, and use schemes. In addition, 17 practitioners treating patients with chronic conditions were interviewed to understand the interrelationships among the aspects and criteria. The fuzzy decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (FDEMATEL) determined the cause-effect interrelationships based on their dependence and driving power. The FDEMATEL results indicated that intelligent connected products and stakeholder communication are the causal and focal attributes of improving digital health service adoption and providing alternative use schemes. For patients and physicians, the driving criteria include managing data, multifunctionality, data reliability, interoperability, patient communication, and resource efficiency. The theoretical and managerial implications are discussed.
Keywords: Digital health service adoption; Factor analysis; Fuzzy decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory; Intelligent connected products; Smart product-service system; Stakeholder communication.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Gogia S.B. Academic Press; 2019. Fundamentals of Telemedicine and Telehealth.
-
- Zhou T., et al. An integrated framework of user experience-oriented smart service requirement analysis for smart product service system development. Adv. Eng. Inf. 2022;51
-
- Cepal N. 2020. Las oportunidades de la digitalización en América Latina frente al Covid-19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources