PLODs: Novel prognostic biomarkers and potential immunotherapy targets for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36820030
- PMCID: PMC9937984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13479
PLODs: Novel prognostic biomarkers and potential immunotherapy targets for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
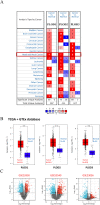
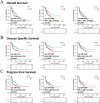
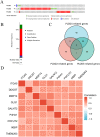
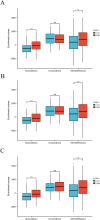
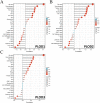
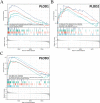
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) comprise a group of malignant tumors arising from the squamous epithelium of the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. HNSCC is the 6th most common cancer in the world, with approximately 650,000 new cases and 400,000 deaths annually. Although survival rates have improved, HNSCC therapy may result in short - or long-term morbidity in approximately 50% of cases. Previous studies have also indicated that the overexpression of procollagen-Lysine, 2-Oxoglutarate 5-Dioxygenases (PLOD) family proteins could lead to certain diseases or even tumors. However, there has been no dedicated evaluation of the relationship between PLOD family members and HNSCC. Here we used data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx), and Human Protein Atlas (HPA) databases to explore the potential role of PLOD family proteins in HNSCC. Our evaluations suggest that increased expression of PLOD family proteins may be associated with poorer prognosis and increased immune infiltration in HNSCC, making these proteins a potential biomarker for personalized treatment of HNSCC.
Keywords: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Immune infiltration; Immunotherapy; PLODs; Prognostic; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Prognostic Value of the PLOD Gene Family in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 21;8:770729. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.770729. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35265665 Free PMC article.
-
FAM3D as a Prognostic Indicator of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Is Associated with Immune Infiltration.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Dec 3;2022:5851755. doi: 10.1155/2022/5851755. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36510584 Free PMC article.
-
Procollagen-Lysine, 2-Oxoglutarate 5-Dioxygenase Family: Novel Prognostic Biomarkers and Tumor Microenvironment Regulators for Lower-Grade Glioma.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Feb 18;16:838548. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.838548. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35250490 Free PMC article.
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Genomics and emerging biomarkers for immunomodulatory cancer treatments.Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Oct;52(Pt 2):228-240. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.01.008. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018. PMID: 29355614 Review.
-
Role and clinical significance of immunogenic cell death biomarkers in chemoresistance and immunoregulation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115509. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115509. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37722193 Review.
Cited by
-
PLOD2 exacerbates cervical squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing p53 by binding to YAP1.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jan;31(1):23. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13388. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39513600 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

