Integrated top-down and bottom-up proteomics mass spectrometry for the characterization of endogenous ribosomal protein heterogeneity
- PMID: 36820077
- PMCID: PMC9937802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2022.11.003
Integrated top-down and bottom-up proteomics mass spectrometry for the characterization of endogenous ribosomal protein heterogeneity
Abstract
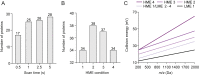
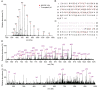
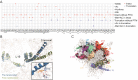
Ribosomes are abundant, large RNA-protein complexes that are the sites of all protein synthesis in cells. Defects in ribosomal proteins (RPs), including proteoforms arising from genetic variations, alternative splicing of RNA transcripts, post-translational modifications and alterations of protein expression level, have been linked to a diverse range of diseases, including cancer and aging. Comprehensive characterization of ribosomal proteoforms is challenging but important for the discovery of potential disease biomarkers or protein targets. In the present work, using E. coli 70S RPs as an example, we first developed a top-down proteomics approach on a Waters Synapt G2 Si mass spectrometry (MS) system, and then applied it to the HeLa 80S ribosome. The results were complemented by a bottom-up approach. In total, 50 out of 55 RPs were identified using the top-down approach. Among these, more than 30 RPs were found to have their N-terminal methionine removed. Additional modifications such as methylation, acetylation, and hydroxylation were also observed, and the modification sites were identified by bottom-up MS. In a HeLa 80S ribosomal sample, we identified 98 ribosomal proteoforms, among which multiple truncated 80S ribosomal proteoforms were observed, the type of information which is often overlooked by bottom-up experiments. Although their relevance to diseases is not yet known, the integration of top-down and bottom-up proteomics approaches paves the way for the discovery of proteoform-specific disease biomarkers or targets.
Keywords: Bottom-up MS; Proteoforms; Ribosomal proteins; Top-down MS.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improving Proteoform Identifications in Complex Systems Through Integration of Bottom-Up and Top-Down Data.J Proteome Res. 2020 Aug 7;19(8):3510-3517. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00332. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Proteome Res. 2020. PMID: 32584579 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Proteoform Post-Translational Modifications by Top-Down and Bottom-Up Mass Spectrometry in Conjunction with Annotations.J Proteome Res. 2023 Oct 6;22(10):3178-3189. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00207. Epub 2023 Sep 20. J Proteome Res. 2023. PMID: 37728997 Free PMC article.
-
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Activated Ion Electron Transfer Dissociation for Large-scale Top-down Proteomics.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019 Dec;30(12):2470-2479. doi: 10.1007/s13361-019-02206-6. Epub 2019 May 9. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019. PMID: 31073891 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling proteoforms: promising follow-up of proteomics for biomarker discovery.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014 Feb;11(1):121-9. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2014.878652. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24437377 Review.
-
Progress in Top-Down Proteomics and the Analysis of Proteoforms.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2016 Jun 12;9(1):499-519. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-071015-041550. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2016. PMID: 27306313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated 4D label-free proteome and SUMOylated proteome in glioma uncover novel pathological mechanisms and pave the way for precision therapy.Cell Insight. 2025 May 19;4(4):100253. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2025.100253. eCollection 2025 Aug. Cell Insight. 2025. PMID: 40606841 Free PMC article.
-
Schisandra chinensis Bee Pollen Extract Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells via Ferroptosis-, Wnt-, and Focal Adhesion-Signaling Pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 2;18:2745-2760. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S461581. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38974120 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis and rescues ischemic myocardium by targeting Caspase-3.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Mar;15(3):101142. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101142. Epub 2024 Nov 12. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40129973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowman J.C., Petrov A.S., Frenkel-Pinter M., et al. Root of the tree: The significance, evolution, and origins of the ribosome. Chem. Rev. 2020;120:4848–4878. - PubMed
-
- Peña C., Hurt E., Panse V.G. Eukaryotic ribosome assembly, transport and quality control. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017;24:689–699. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

