The Comprehensive Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) Protein in Different Tumors: A Pan-Cancer Analysis
- PMID: 36820147
- PMCID: PMC9938709
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S386898
The Comprehensive Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) Protein in Different Tumors: A Pan-Cancer Analysis
Abstract
Background: HMGB1 is a highly conserved nuclear protein widely expressed in mammalian cells. This study aimed to comprehensively investigate the roles and mechanisms of HMGB1 in different tumors.
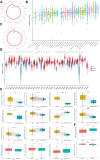
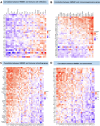
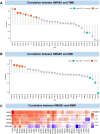
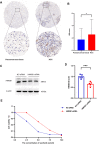
Methods: Original data on HMGB1 expression, localization, potential interacting proteins, genetics were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas, Genotype-Tissue Expression, Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia, Human Protein Atlas, Compartmentalized Protein-Protein Interaction and cBioPortal databases. Then, correlation between HMGB1 expression levels and tumor stage, prognosis, potential pathways, tumor microenvironment, ESTIMATE score, immune-related genes, immune cell infiltration, microsatellite instability, tumor mutation burden, or anti-tumor drug resistance was investigated. The above results consistently indicated that high expression of HMGB1 protein may be related to clinical prognosis of HCC patients. Therefore, clinical tissues of HCC patients were selected to verify the differential expression of HMGB1 protein in HCC. The sensitivity of HMGB1-siRNA transfected HepG2 cells to sorafenib was assessed.
Results: HMGB1 was found to be differentially expressed in many tumors and normal tissues. HMGB1 was mainly located in the nucleus and might interact with proteins such as TLR2 and TLR4. Furthermore, HMGB1 expression was closely related to tumor stage, prognosis, tumor microenvironment, immune-related genes, immune cell infiltration, microsatellite instability, tumor mutation burden, and anti-tumor drug resistance and might be involved in different pathways of various tumors. Immunohistochemistry results further verified the differential expression of HMGB1 in HCC and paracancerous tissues. HMGB1-siRNA transfected HepG2 cells had a tendency to be more insensitive to sorafenib treatment compared to the control group.
Conclusions: HMGB1 was differentially expressed in most tumors and normal tissues, and was closely related to the clinical stage, prognosis, immune infiltration, tumor microenvironment, and drug resistance of tumors. Therefore, HMGB1 may serve as a novel biomarker for predicting tumor prognosis, efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors, and a potential target for anti-tumor therapy.
Keywords: bioinformatics; high mobility group box 1; pan-cancer analysis; prognosis; tumor.
© 2023 Guan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic function of HMGB1 in human tumors.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Nov 7;40:101851. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101851. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39582753 Free PMC article.
-
[Pan-cancer analysis of the expression pattern of long non-coding RNA MIR22HG].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Apr 20;42(4):473-485. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.04.03. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35527483 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Pan-cancer analysis of trophinin-associated protein with potential implications in clinical significance, prognosis, and tumor microenvironment in human cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 7;12:971618. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.971618. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36419876 Free PMC article.
-
A Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals the Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Value of Stanniocalcin-2 (STC2).Front Genet. 2022 Jul 22;13:927046. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.927046. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35937984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of HMGB1 expression with clinicopathological significance and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis and literature review.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 30;9(10):e110626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110626. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25356587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of serum HMGB1 and IDO in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients: potential clinical auxiliary diagnostic markers and immunotherapeutic targets.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 9;14:1452282. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1452282. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39314628 Free PMC article.
-
The examination of in vitro photosensitizing efficacy of aloe-emodin loaded liposome following photodynamic therapy on melanoma cell lines.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 6;15(1):28833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14777-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770046 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

