Enhanced leachate phytodetoxification test combined with plants and rhizobacteria bioaugmentation
- PMID: 36820189
- PMCID: PMC9938419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12921
Enhanced leachate phytodetoxification test combined with plants and rhizobacteria bioaugmentation
Abstract
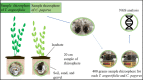
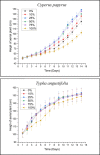
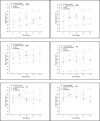
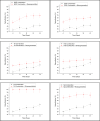
Plant combination and rhizobacterial bioaugmentation are the modification of constructed wetlands (CWs) to promote the detoxification of leachate. In this study, characterization of leachate was carried out to ensure the maximum concentration of leachate that did not affect the plant's growth. Herein, the identification of leachate-resistant rhizobacteria is used to determine the type of bacteria that is resistant and has the potential for leachate processing in the next step. The phytodetoxification test is carried out by comparing the addition of rhizobacteria and without the addition of rhizobacteria to detox leachate parameter Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD), Total Suspended Solid (TSS), Total Nitrogen (TN), Cadmium (Cd), and Mercury (Hg). Results showed that used plants could still live in the largest leachate concentration of 100%. The rhizobacteria that were identified and bioaugmented in the reactor were Bacillus cereus, Nitrosomonas communis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Phytodetoxification test by a single plant showed the efficiency ranged between 40% and 70%. The addition of rhizobacterial bioaugmentation and plant combination can improve the percentage of COD 80.47%, BOD 84.05%, TSS 80.05%, TN 75.58%, Cd 99.96%, and Hg 90%. These modifications are very influential for leachate detoxification through plant uptake and rhizodegradation processes.
Keywords: Bacillus cereus; Cyperus papyrus; Nitrosomonas communis; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Typha angustifolia.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of leachate through constructed wetlands using Typha angustifolia in combination with catalytic ozonation on Fe-zeolite A.Int J Phytoremediation. 2021;23(8):809-817. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2020.1858753. Epub 2020 Dec 12. Int J Phytoremediation. 2021. PMID: 33307731
-
Landfill leachate treatment using sub-surface flow constructed wetland by Cyperus haspan.Waste Manag. 2012 Jul;32(7):1387-93. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Mar 26. Waste Manag. 2012. PMID: 22456086
-
Treatment of nanofiltration concentrate of landfill leachate using advanced oxidation processes incorporated with bioaugmentation.Environ Pollut. 2023 Feb 1;318:120827. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120827. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 36509353
-
Application of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in tropical and subtropical regions (2000-2013).J Environ Sci (China). 2015 Apr 1;30:30-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2014.10.013. Epub 2015 Feb 24. J Environ Sci (China). 2015. PMID: 25872707 Review.
-
Removal of organics in constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow: a review of the field experience.Sci Total Environ. 2009 Jun 15;407(13):3911-22. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.08.032. Epub 2008 Sep 25. Sci Total Environ. 2009. PMID: 18822446 Review.
Cited by
-
Constructed wetlands combined with microbial fuel cells (CW-MFCs) as a sustainable technology for leachate treatment and power generation.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 11;14(44):32073-32100. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04658g. eCollection 2024 Oct 9. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39399250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphophysiological Adaptations of Aquatic Macrophytes in Wetland-Based Sewage Treatment Systems: Strategies for Resilience and Efficiency under Environmental Stress.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 14;13(20):2870. doi: 10.3390/plants13202870. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed F., Fakhruddin A.N.M., Fardous Z., Chowdhury M.A.Z., Rahman M.M., Kabir M.M. Accumulation and translocation of chromium (Cr) and lead (Pb) in chilli plants (capsicum annuum L.) grown on artificially contaminated soil. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2021;20:63–70. doi: 10.46488/NEPT.2021.V20I01.007. - DOI
-
- Ahmed F., Fakhruddin A.N.M., Fardous Z., Chowdhury M.A.Z., Rahman M.M., Kabir M.M. Accumulation and translocation of chromium (Cr) and lead (Pb) in chilli plants (capsicum annuum L.) grown on artificially contaminated soil. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2021;20:63–70. doi: 10.46488/NEPT.2021.V20I01.007. - DOI
-
- Ahmed H.A., Ali S.G., Abdul-raouf U.M., Awad H., Mohamed A. Isolation , characterization and molecular identification of Bacillus thuringiensis Alex-13 isolated from Egypt against Spodoptera littoralis. International Journal of Microbiology and Allied Sciences. 2015;2:34–44.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

